HP BL260c HP BladeSystem c-Class Site Planning Guide - Page 13
Computer room safety, Installation and maintenance precautions, Fire protection, Fire suppression
 |
UPC - 883585668663
View all HP BL260c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
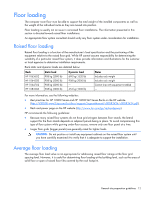
Computer room safety Inside the computer room, fire protection and adequate lighting (for equipment servicing) are important safety considerations. Federal and local safety codes that govern equipment installations. Installation and maintenance precautions To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment when installing, maintaining, or servicing Enterprise products, observe the following general precautions: • Provide overhead clearance for fire sprinkler devices-A minimum clearance is required between the top of the rack and any fire protection sprinkler devices. Check the local building code for details. • Be aware of power voltages and use trained personnel-Some Enterprise products are capable of producing hazardous voltages and hazardous energy levels. The installation of internal options and routine maintenance and service of these products should be performed only by individuals who are familiar with the procedures, precautions, and hazards associated with this type of equipment. • Secure all equipment-Rack equipment should be operated only with all enclosures in place and properly secured. Always refer to the equipment installation guide and observe all applicable warnings and precautions. • Follow manufacturer instructions-Always refer to the individual equipment installation instructions for any special considerations when installing equipment in a rack. Fire protection The National Fire Protection Association's Standard for the Protection of Electronic Computer Data Processing Equipment, NFPA 75, contains information on safety monitoring equipment for computer rooms. Most computer room installations are equipped with the following fire protection devices: • Smoke detectors • Fire and temperature alarms • Fire extinguishing system • Air handling (plenum) space that is segmented from the remainder of the building Additional safety devices: • Circuit breakers • An emergency power cutoff switch • Devices specific to geographic location (such as earthquake protection) Fire suppression Though fires in computer rooms are rare, they are a critical safety and business consideration. HP recommends the use of gaseous agents as primary fire control, with water as a backup system. Gaseous agents include CO2, and Halon substitutes, like Intergen. Where fire suppression using water is dictated, HP recommends the use of dry pipe water valving, with suitably rated temperature heads. Dry pipe water valving lowers the business risks associated with accidental water pipe discharge. General site preparation guidelines 13