MSI 975X PLATINUM User Guide - Page 112
RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks, RAID 0 Striping, RAID 1 Mirroring, JBOD Concatenate
 |
UPC - 816909035759
View all MSI 975X PLATINUM manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
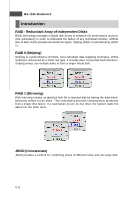
MS-7246 Mainboard Introduction RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks RAID technology manages multiple disk drives to enhance I/O performance and provide redundancy in order to withstand the failure of any individual member, without loss of data. RAID provides two RAID Set types, Striping (RAID 0) and Mirroring (RAID 1). RAID 0 (Striping) Striping is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. W hile Striping is discussed as a RAID Set type, it actually does not provide fault tolerance. Striping arrays use multiple disks to form a larger virtual disk. RAID 1 (Mirroring) Disk mirroring creates an identical twin for a selected disk by having the data simultaneously written to two disks. This redundancy provides instantaneous protection from a single disk failure. If a read failure occurs on one drive, the system reads the data from the other drive. JBOD (Concatenate) JBOD provides a method for combining drives of different sizes into one large disk C-2