eMachines ET1161 8513042 - eMachines Desktop Computer User Guide - Page 54
Wireless Ethernet standards, Using an access point, Equipment you need for an access point-based
 |
View all eMachines ET1161 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 54 highlights
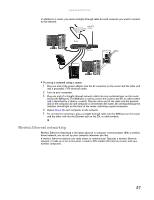
Chapter 5: Networking Your Computer Wireless Ethernet standards Current wireless Ethernet standards include the following: • 802.11a - 54Mbps • 802.11b - 11Mbps • 802.11g - 54Mbps • 802.11n - 540Mbps Speed is not the only issue if you decide to use equipment with different standards. Compatibility can also be an issue. Take the following into consideration when you purchase wireless equipment: Access point Wireless cards supported 802.11a 802.11a only 802.11b 802.11b only 802.11g 802.11b and 802.11g 802.11n 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n Using an access point An access point is a small electronic device that serves as the central control point for your network. You connect your modem to the access point, set up a network connection, then browse the Internet, send e-mail, share files and folders with other networked computers, and access other devices, like a printer or scanner. Cable or DSL modem 48 Access point Equipment you need for an access point-based network Tip When you buy your access point, make sure it has: • IEEE 802.11n support. 802.11n is the fastest method for wireless communications. 802.11n is compatible with the older IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11b formats but not with the competing IEEE 802.11a format. Make sure that you get the correct format that matches your computer. • DHCP server/dynamic IP address assignment capability that makes it easier to set up and access your network. • Internet security features like a firewall to keep intruders out of your network. • Wireless security features like SecureEasySetup™ or 128-bit WEP encryption. For a wireless Ethernet network you need: • Your Gateway computer with wireless networking installed • A broadband Internet connection (optional) • An access point