Alcatel OS6400-48 Hardware User Guide - Page 20
Hot Swapping, Hardware Monitoring, Automatic Monitoring, User-Driven Monitoring
 |
View all Alcatel OS6400-48 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
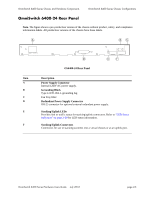
Availability Features OmniSwitch 6400 Series Hot Swapping Hot swapping refers to the action of adding, removing, or replacing components without powering off switches or disrupting other components.This feature facilitates hardware upgrades and maintenance and allows users to easily replace components in the unlikely event of hardware failure. The following hardware components can be hot swapped: • Backup power supply • Backup power supply connector cables • SFPs For instructions on hot swapping backup power supplies, refer to Chapter 3, "Mounting OS6400 Switches." For instructions on hot swapping combo connector SFPs, refer to the OmniSwitch Transceivers Guide. Hardware Monitoring Automatic Monitoring Automatic monitoring refers to the switch's built-in sensors that automatically monitor operations. If an error is detected (e.g., over-threshold temperature), the switch immediately sends a trap to the user. The trap is displayed on the console in the form of a text error message. (In the case of an over-threshold temperature condition, the chassis displays an amber TMP LED in addition to sending a trap.) LEDs LEDs, which provide visual status information, are provided on the chassis front panel. LEDs are used to indicate conditions such as hardware and software status, temperature errors, link integrity, data flow, etc. For detailed LED descriptions, refer to Chapter 2, "OmniSwitch 6400 Series Chassis and Hardware Components." User-Driven Monitoring User-driven hardware monitoring refers to CLI commands that are entered by the user in order to access the current status of hardware components. The user enters "show" commands that output information to the console. Monitoring information for chassis components, such as the optional back up power supply, chassis temperature sensor, and chassis fans is provided in Chapter 2, "OmniSwitch 6400 Series Chassis and Hardware Components." The show commands for all the features are described in detail in the OmniSwitch CLI Reference Guide. page 1-4 OmniSwitch 6400 Series Hardware Users Guide July 2010