Cisco 3825 Software Configuration Guide - Page 15
Cisco Iub Optimization over IP, Intelligent Cell Site IP Services, Cell Site Points-of-Presence (POPs) - vpn
 |
UPC - 746320981505
View all Cisco 3825 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
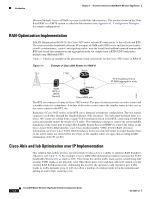
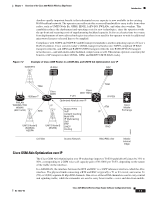
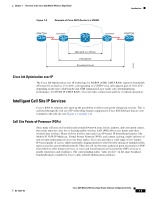
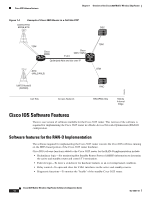
Chapter 1 Overview of the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router Figure 1-3 Example of Cisco 3825 Router in a PWE3f Introduction ATM/TDM xconnect xconnect ATM/TDM 201865 MPLS/IP or L2TPv3 Pseudowire Emulated Circuit Cisco Iub Optimization over IP The Cisco Iub Optimization over IP technology for R4/R99 (ATM) UMTS RANs improves bandwidth efficiency by as much as 15 to 40%, corresponding to a UMTS voice call capacity gain of 18 to 67%, depending on the type of Iub header and ATM Adaptation Layer traffic sub-cell multiplexing performance. For R5/R6 IP UMTS RANs, Cisco provides compression and low-overhead encryption. Intelligent Cell Site IP Services Cisco's RAN-O solutions also open up the possibility to deliver new profit-enhancing services. This is achieved through the rich set of IP networking features supported in Cisco IOS Software that are now extended to the cell site (see Figure 1-4 on page 1-6). Cell Site Points-of-Presence (POPs) Since many cell sites are located in and around downtown areas, hotels, airports, and convention centers, they make attractive sites for co-locating public wireless LAN (PWLAN) access points and other wireless data overlays. Many of these wireless data radios are IP-based. IP networking features, like Mobile IP, VoIP, IP Multicast, Virtual Private Network (VPN), and content caching, enable delivery of new revenue-generating services over these radios. Cisco also provides a wide range of low-latency IP-based quality of service (QoS) and traffic shaping models to allow flexible mixing of multiple traffic types across the same backhaul network. Thus, the cell site becomes a physical point of presence or POP from which to offer hotspot services, or voice and wired Internet service provider (ISP) services to nearby enterprises and residences. The corresponding traffic "rides for free" on the spare backhaul bandwidth made available by Cisco's Abis and Iub Optimization solutions. OL-15667-03 Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router Software Configuration Guide 1-5