Compaq dc7100 HP Compaq dc71xx and dx61xx Series Business Desktop Computers Te - Page 116
Audio Subsystem, Mic In, Line In, Headphones Out, Line Out
 |
View all Compaq dc7100 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 116 highlights
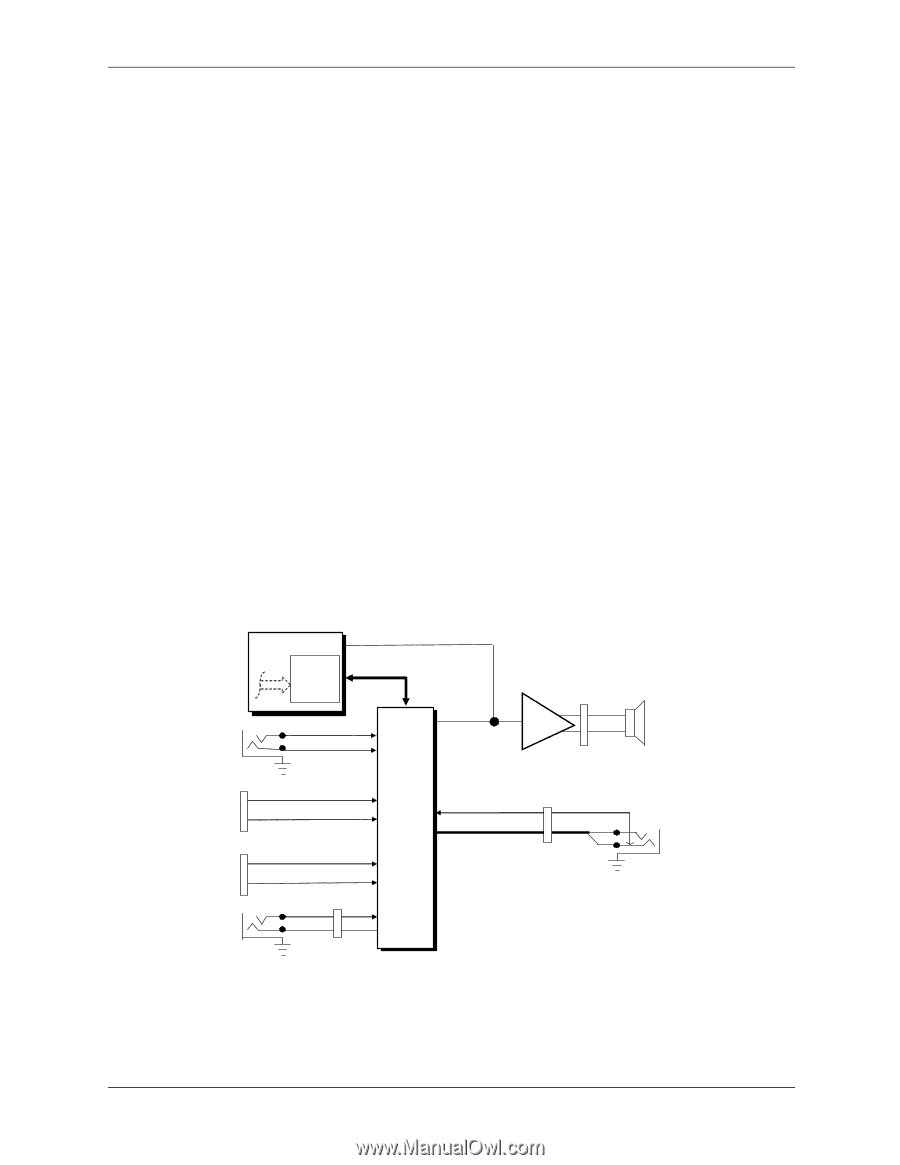
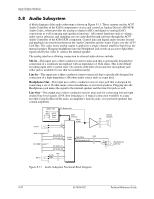
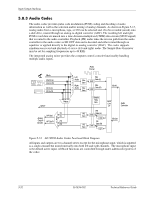
Input/Output Interfaces 5.8 Audio Subsystem A block diagram of the audio subsystem is shown in Figure 5-11. These systems use the AC97 Audio Controller of the 82801 component to access and control an Analog Devices AD1981B Audio Codec, which provides the analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog (DAC) conversions as well as mixing and equalizer functions. All control functions such as volume, audio source selection, and sampling rate are controlled through software through the AC97 Audio Controller of the 82801 ICH component. Control data and digital audio streams (record and playback) are transferred between the Audio Controller and the Audio Codec over the AC97 Link Bus. The codec mono analog output is applied to a single-channel amplifier that drives the internal speaker. Plugging headphones into the Headphone jack results in an active Spkr Mute signal used by the codec to ,silence the internal speaker The analog interfaces allowing connection to external audio devices include: Mic In-This input uses a three-conductor (stereo) mini-jack that is specifically designed for connection of a condenser microphone with an impedance of 10-K ohms. This is the default recording input after a system reset. On systems with both a front and rear microphone jack either jack is available for use (but not simultaneously). Line In-This input uses a three-conductor (stereo) mini-jack that is specifically designed for connection of a high-impedance (10k-ohm) audio source such as a tape deck. Headphones Out-This input uses a three-conductor (stereo) mini-jack that is designed for connecting a set of 16-ohm (nom.) stereo headphones or powered speakers. Plugging into the Headphones jack mutes the signal to the internal speaker and the Line Out jack as well. Line Out-This output uses a three-conductor (stereo) mini-jack for connecting left and right channel line-level signals (20-K ohm impedance). A typical connection would be to a tape recorder's Line In (Record In) jacks, an amplifier's Line In jacks, or to powered speakers that contain amplifiers. Line In 82801 ICH PCI Bus AC'97 Audio Cntlr. PC Beep Audio AC97 Link Bus Mono Audio (L) (R) TDA 7056 Internal Speaker P6 + - AUX In Header P11 [1] Aux Audio (L) Aux Audio (R) Audio Codec Spkr Mute P23 HP Out Audio (L/R) (L) (R) CD ROM Header P7 [2] CD Audio (L) CD Audio (R) Mic In P23 Audio Bias Headphones/ Line Out Figure 5-11. Audio Subsystem Functional Block Diagram 5-30 361834-002 Technical Reference Guide