Dell PowerEdge M610 Web Tools Administrator’s Guide - Page 214
Supported platforms for iSCSI, Common iSCSI Target Gateway Admin functions, Terminology, Export
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge M610 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 214 highlights
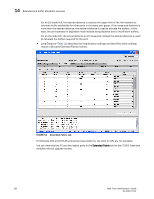
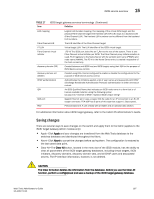
15 iSCSI service overview DRAFT: BROCADE CONFIDENTIAL Supported platforms for iSCSI The iSCSI target gateway service is supported on the Brocade 48000 director with CP blades running Fabric OS v5.2.0 and later releases, and configured with an FC4-16IP blade. Common iSCSI Target Gateway Admin functions You can right-click on the table content in the window to access Export, Copy, and Search options: NOTE You must accept the Brocade Certificate at the beginning of the login to Web Tools to enable the functionality of Export and Copy. • Click Export Row or Export Table to save the contents to a tab-delimited file. For CHAP, the secret is still encrypted. • Click Copy Row or Copy Table to copy the contents in tab-delimited text format to a file. • Click Search to search for a specific text string in the table. Enter a text string in the box that displays in the table and press Enter. This is an incremental search and allows 24 maximum characters including the wildcard characters: question mark (?) and asterisk (*). The first row containing the text string is highlighted. To find the next match, press the down arrow. To find the previous match, press the up arrow. If the text is not found in the table, the text displays in red color. Terminology iSCSI target gateway services require you to understand some additional terminology. Table 17 shows the terms that are used in this document to explain how the iSCSI target gateway is implemented. TABLE 17 iSCSI target gateway services terminology Term Definition iSCSI iSCSI target gateway iSCSI port iSCSI virtual target iSCSI initiator iSCSI session Internet-SCSI. A transport carrier of the SCSI protocol over IP. An intermediate device in the network that allows the iSCSI initiators in an IP SAN to access and utilize storage in a Fibre Channel SAN. the FC4-16IP AP blade in a Brocade 48000 director functions as an iSCSI target gateway. A special GbE port used for iSCSI only. A Fibre Channel virtual initiator is created behind each iSCSI port running as a proxy Fibre Channel initiator. A unique target device in the IP SAN that contains LUNs from the real Fibre Channel targets and is identified by an IQN. A device that begins an iSCSI transaction by issuing a command to another device (the iSCSI target), giving it a task to perform. Typically, an iSCSI host adapter is the initiator but targets can also become initiators. An iSCSI session is the basic communication "pipe" from an iSCSI initiator to an iSCSI target. A session is a group of TCP/IP connections that link an initiator with a target (loosely equivalent to a SCSI I-T nexus). 186 Web Tools Administrator's Guide 53-1001772-01