HP LaserJet P1500 Service Manual - Page 44
Step 2: Laser beam exposure, Step 3: Developing,
 |
View all HP LaserJet P1500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
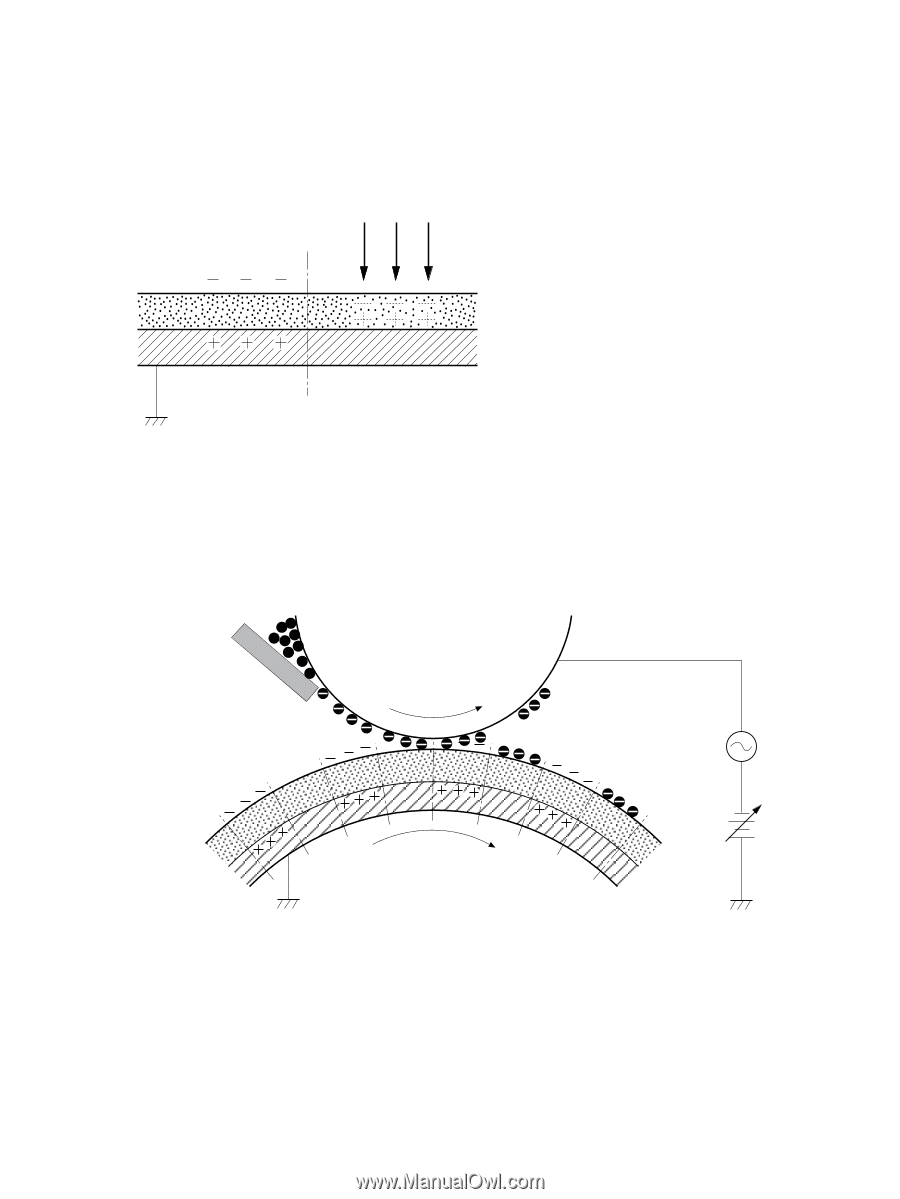
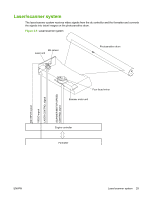
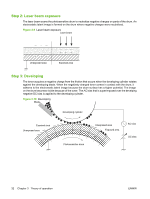
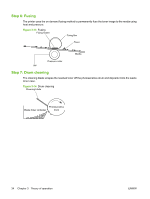
Step 2: Laser beam exposure The laser beam scans the photosensitive drum to neutralize negative charges on parts of the drum. An electrostatic latent image is formed on the drum where negative charges were neutralized. Figure 3-9 Laser beam exposure Laser beam Unexposed area Exposed area Step 3: Developing The toner acquires a negative charge from the friction that occurs when the developing cylinder rotates against the developing blade. When the negatively charged toner comes in contact with the drum, it adheres to the electrostatic latent image because the drum surface has a higher potential. The image on the drum becomes visible because of the toner. The AC bias that is superimposed over the develping negative DC bias is applied to the developing cylinder. Figure 3-10 Developing Blade Developing cylinder Exposed area Unexposed area Photosensitive drum Unexposed area Exposed area AC bias DC bias 32 Chapter 3 Theory of operation ENWW