Netgear DG834G DG834G Original Reference Manual - Page 170
Is WPA Perfect?, Product Support for WPA - network security key
 |
UPC - 606449029918
View all Netgear DG834G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 170 highlights
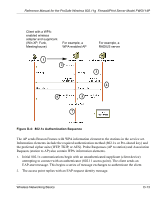
Reference Manual for the ProSafe Wireless 802.11g Firewall/Print Server Model FWG114P Is WPA Perfect? WPA is not without its vulnerabilities. Specifically, it is susceptible to denial of service (DoS) attacks. If the access point receives two data packets that fail the message integrity code (MIC) within 60 seconds of each other, then the network is under an active attack, and as a result, the access point employs counter measures, which include disassociating each station using the access point. This prevents an attacker from gleaning information about the encryption key and alerts administrators, but it also causes users to lose network connectivity for 60 seconds. More than anything else, this may just prove that no single security tactic is completely invulnerable. WPA is a definite step forward in WLAN security over WEP and has to be thought of as a single part of an end-to-end network security strategy. Product Support for WPA Starting in August, 2003, NETGEAR, Inc. wireless Wi-Fi certified products will support the WPA standard. NETGEAR, Inc. wireless products that had their Wi-Fi certification approved before August, 2003 will have one year to add WPA so as to maintain their Wi-Fi certification. WPA requires software changes to the following: • Wireless access points • Wireless network adapters • Wireless client programs Supporting a Mixture of WPA and WEP Wireless Clients is Discouraged To support the gradual transition of WEP-based wireless networks to WPA, a wireless AP can support both WEP and WPA clients at the same time. During the association, the wireless AP determines which clients use WEP and which clients use WPA. The disadvantage to supporting a mixture of WEP and WPA clients is that the global encryption key is not dynamic. This is because WEP-based clients cannot support it. All other benefits to the WPA clients, such as integrity, are maintained. However, a mixed mode supporting WPA and non-WPA clients would offer network security that is no better than that obtained with a non-WPA network, and thus this mode of operation is discouraged. D-16 Wireless Networking Basics