D-Link DES-1210-52 Product Manual - Page 59
Security > ARP Spoofing Prevention, Security > Trusted Host
 |
UPC - 790069327827
View all D-Link DES-1210-52 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 59 highlights
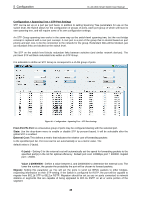
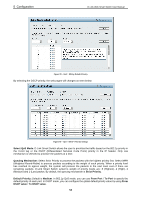
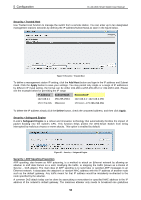
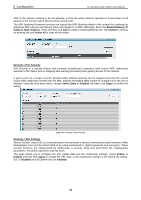
5 Configuration D-Link Web Smart Switch User Manual Security > Trusted Host Use Trusted Host function to manage the switch from a remote station. You can enter up to ten designated management stations networks by defining the IP address/Subnet Mask as seen in the figure below. Figure 91 Security > Trusted Host To define a management station IP setting, click the Add Host button and type in the IP address and Subnet mask. Click the Apply button to save your settings. You may permit only single or a range of IP addresses by different IP mask setting, the format can be either 192.168.1.1/255.255.255.0 or 192.168.0.1/24. Please see the example below for permitting the IP range IP Address Subnet Mask Permitted IP 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1~192.168.0.255 172.17.5.215 255.0.0.0 172.0.0.1~172.255.255.255 To delete the IP address simply click the Delete button, check the unwanted address, and then click Apply. Security > Safeguard Engine D-Link's Safeguard Engine is a robust and innovative technology that automatically throttles the impact of packet flooding into the switch's CPU. This function helps protect the Web-Smart Switch from being interrupted by malicious viruses or worm attacks. This option is enabled by default. Figure 92 - Security > Safeguard Engine Security > ARP Spoofing Prevention ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a method to attack an Ethernet network by allowing an attacker to sniff data frames on a LAN, modifying the traffic, or stopping the traffic (known as a Denial of Service - DoS attack). The main idea of ARP spoofing is to send fake or spoofed ARP messages to an Ethernet network. It associates the attacker's or random MAC address with the IP address of another node such as the default gateway. Any traffic meant for that IP address would be mistakenly re-directed to the node specified by the attacker. A common DoS attack today can be done by associating a nonexistent or specified MAC address to the IP address of the network's default gateway. The malicious attacker only needs to broadcast one gratuitous 53