Foxconn A7GM-S English Manual. - Page 39
► Channel Interleaving, ► Enable Clock to All DIMMs, ► MemClk Tristate C3/ALTVID, ► Memory Hole - ram
 |
View all Foxconn A7GM-S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
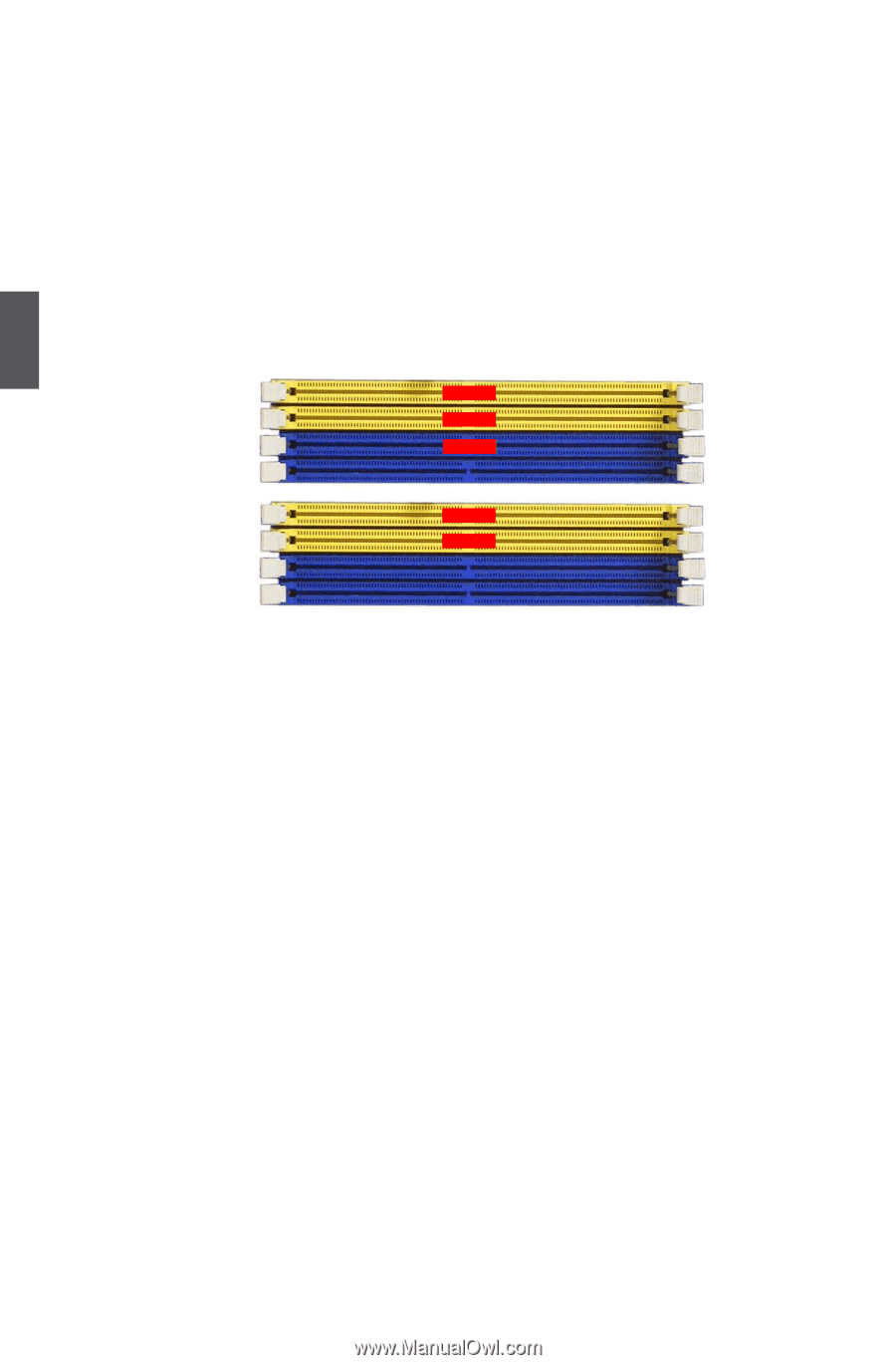
However, bank interleaving only works if the addresses requested consecutively are not in the same bank. ► Channel Interleaving Dual channel (Interleaved) mode offers the highest throughput for real world applications. Dual channel mode is enabled when the installed memory capacities of both DIMM channels are equal. If different speed DIMMs are used between channels, the slowest memory timing will be used. To achieve Dual Channel Interleaving mode, the following conditions must be met: Matched DIMM configuration in each channel Same Density (128MB, 256MB, 512MB, etc.) Channel 0 DIMM1 Channel 1 DIMM2 Channel 0 DIMM3 Channel 1 DIMM4 512MB 1GB 512MB Channel 0 DIMM1 Channel 1 DIMM2 Channel 0 DIMM3 Channel 1 DIMM4 1GB 1GB 3 Matched in both Channel 0 and Channel 1 memory channels ► Enable Clock to All DIMMs This setting is to control EMI. When disabled, the system will turn off clock on the empty DIMM slots and to reduce EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference). ► MemClk Tristate C3/ALTVID Enables the DDR memory clocks to be tristated when alternate VID mode is enabled. ► Memory Hole Remapping This item is used to enable/disable memory remapping around memory hole. PCI doesn't actually care much which addresses are used, but by convention the PC platform puts them at the top of the 32-bit address space. For many years it wasn't possible or practical to put that much RAM into a PC. But now it is, so it's up to the memory controller and host bridge to figure out what to do. Many systems cause that high RAM to simply be ignored, resulting in the loss of effective RAM. More complex systems will take the RAM that would occupy that 3.5-4GB address space and re-map it into the 4.0-4.5 address space. The RAM doesn't care because it's just an array of storage cells, it's up to the memory controller to associate addresses with those storage cells. Of course, that only works if you're using a 64-bit (or 32bit physical address extension (PAE) enabled) OS that can deal with physical addresses larger than 32 bits. Once this option is enabled, the BIOS can see 4096MB of memory. ► DCT Unganged Mode DCT stands for DRAM Controller. Ganged refers to the use of both DRAM controllers within a memory controller acting in con- 32