HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches IP Multicast Configuration - Page 167
Inter-domain multicast delivery through MSDP, Source-side MSDP peer, Receiver-side, MSDP peer
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 167 highlights
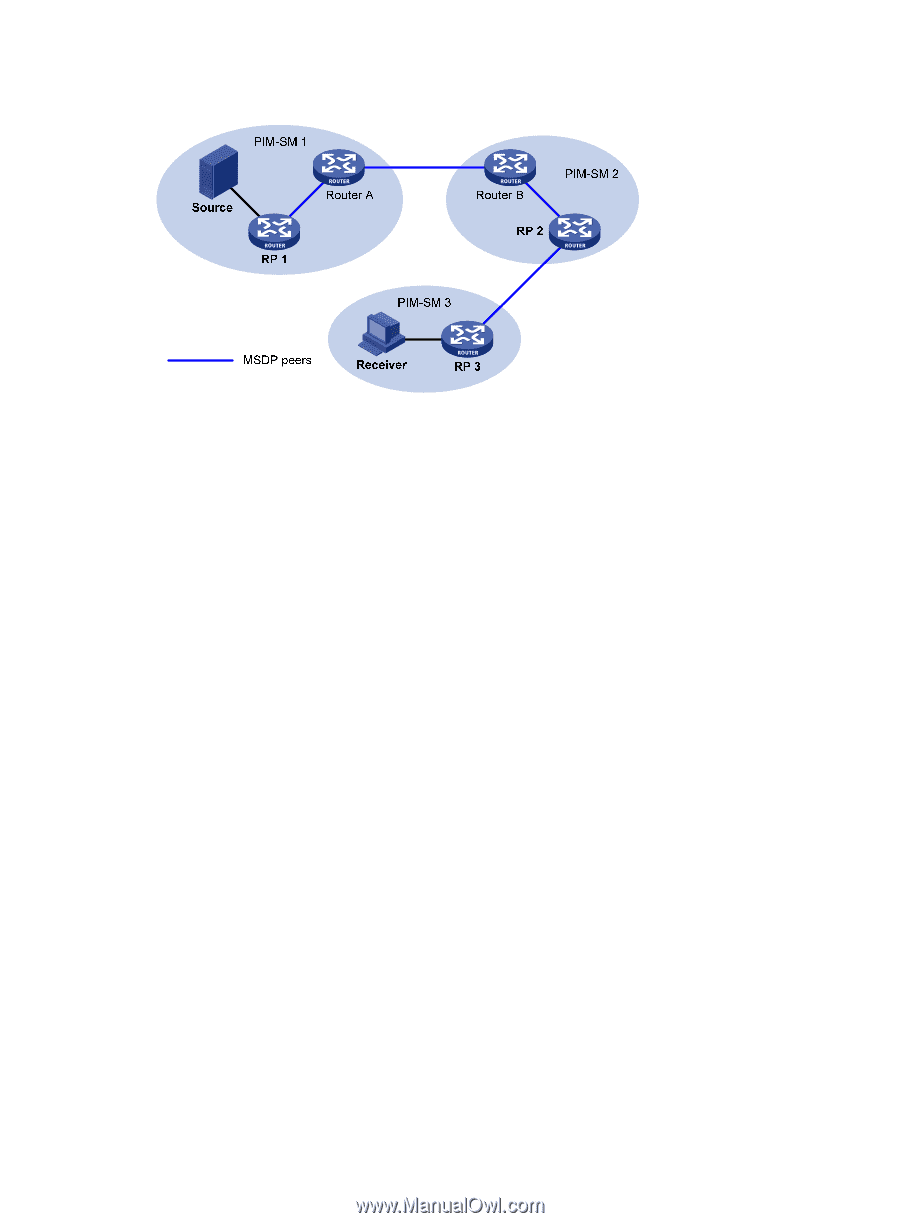
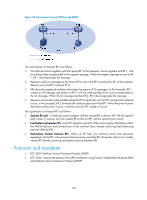
Figure 50 Where MSDP peers are in the network As shown in Figure 50, an MSDP peer can be created on any PIM-SM router. MSDP peers created on PIM-SM routers that assume different roles function differently. 1. MSDP peers on RPs include the following types: { Source-side MSDP peer-The MSDP peer nearest to the multicast source (Source), typically the source-side RP, like RP 1. The source-side RP creates SA messages and sends the messages to its remote MSDP peer to notify the MSDP peer of the locally registered multicast source information. A source-side MSDP peer must be created on the source-side RP. Otherwise it will not be able to advertise the multicast source information out of the PIM-SM domain. { Receiver-side MSDP peer-The MSDP peer nearest to the receivers, typically the receiver-side RP, like RP 3. After receiving an SA message, the receiver-side MSDP peer resolves the multicast source information carried in the message and joins the SPT rooted at the source across the PIM-SM domain. When multicast data from the multicast source arrives, the receiver-side MSDP peer forwards the data to the receivers along the RPT. { Intermediate MSDP peer-An MSDP peer with multicast remote MSDP peers, like RP 2. An intermediate MSDP peer forwards SA messages received from one remote MSDP peer to other remote MSDP peers, functioning as a relay of multicast source information. 2. MSDP peers created on common PIM-SM routers (other than RPs) Router A and Router B are MSDP peers on common multicast routers. Such MSDP peers just forward received SA messages. In a PIM-SM network running the BSR mechanism, the RP is dynamically elected from C-RPs. To enhance network robustness, a PIM-SM network typically has more than one C-RP. As the RP election result is unpredictable, MSDP peering relationship must be built among all C-RPs so that the winner C-RP is always on the "MSDP interconnection map," and loser C-RPs will assume the role of common PIM-SM routers on the "MSDP interconnection map." Inter-domain multicast delivery through MSDP As shown in Figure 51, an active source (Source) exists in the domain PIM-SM 1, and RP 1 has learned the existence of Source through multicast source registration. If RPs in PIM-SM 2 and PIM-SM 3 also seek the specific location of Source so that receiver hosts can receive multicast traffic that the source sends, HP recommends you to establish MSDP peering relationship between RP 1 and RP 3 and between RP 3 and RP 2, respectively. 156