HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches IP Multicast Configuration - Page 321
Configuring C-BSRs for IPv6 admin-scope zones, Configuring IPv6 multicast source registration
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 321 highlights
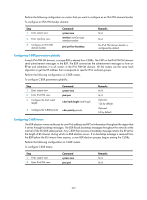
Configuring C-BSRs for IPv6 admin-scope zones In a network with IPv6 administrative scoping enabled, BSRs are elected from C-BSRs specific to different Scope field values. The C-RPs in the network send advertisement messages to the specific BSR. The BSR summarizes the advertisement messages to form an RP-set and advertises it to all routers in the specific admin-scope zone. All the routers use the same hash algorithm to get the RP address corresponding to the specific IPv6 multicast group. You can configure the hash mask length and C-BSR priority globally and in an IPv6 admin-scope zone. • The values configured in the IPv6 admin-scope zone have preference over the global values. • If you do not configure these parameters in the IPv6 admin-scope zone, the corresponding global values will be used. For configuration of global C-BSR parameters, see "Configuring C-BSR parameters globally." Perform the following configuration on the routers that you want to configure as C-BSRs in IPv6 admin-scope zones. To configure a C-BSR for an IPv6 admin-scope zone: Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Enter IPv6 PIM view. pim ipv6 N/A c-bsr scope { scope-id | admin-local | 3. Configure a C-BSR for an global | organization-local | site-local } No C-BSRs are configured for an IPv6 admin-scope zone. [ hash-length hash-length | priority IPv6 admin-scope zone by default. priority ] * Configuring IPv6 multicast source registration Within an IPv6 PIM-SM domain, the source-side DR sends register messages to the RP, and these register messages have different IPv6 multicast source or IPv6 multicast group addresses. You can configure a filtering rule to filter register messages so that the RP can serve specific IPv6 multicast groups. If the filtering rule denies an (S, G) entry, or if the filtering rule does not define an action for this entry, the RP will send a register-stop message to the DR to stop the registration process for the IPv6 multicast data. In view of information integrity of register messages in the transmission process, you can configure the device to calculate the checksum based on the entire register messages. However, to reduce the workload of encapsulating data in register messages and for the sake of interoperability, HP does not recommend this method of checksum calculation. When receivers stop receiving data addressed to a certain IPv6 multicast group through the RP (which means that the RP stops serving the receivers of that IPv6 multicast group), or when the RP starts receiving IPv6 multicast data from the IPv6 multicast source along the SPT, the RP sends a register-stop message to the source-side DR. After receiving this message, the DR stops sending register messages encapsulated with IPv6 multicast data and starts a register-stop timer. Before the register-stop timer expires, the DR sends a null register message (a register message without multicast data) to the RP. If the DR receives a register-stop message during the register probe time, it will reset its register-stop timer. Otherwise, the DR starts sending register messages with encapsulated data again when the register-stop timer expires. The register-stop timer is set to a random value chosen uniformly from the interval (0.5 times register_suppression_time, 1.5 times register_suppression_time) minus register_probe_time. 310