HP 6125G HP Networking guide to hardening Comware-based devices - Page 27
Port security
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
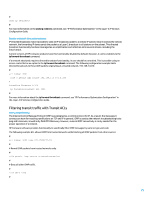
After receiving a packet, an IP source guard-enabled port obtains the key attributes (source IP address, source MAC address, and VLAN tag) of the packet and then looks up the binding entries of the IP source guard for a match. If there is a match, the port forwards the packet; otherwise, the port discards the packet. You can enable this feature on a port connected to terminals to block illegal access (such as IP spoofing) and improve port security. HP IP source guard supports static and dynamic entries. You can configure static entries in scenarios where there are only a few hosts in a LAN and their IP addresses are manually configured. For example, you can configure a static entry on a port that connects a server so that the port receives and sends packets from/to only the server. Following is an example of static entry configuration: # # Configure Ethernet 1/2 on Device B to allow only packets from host A with MAC address 00010203-0406 and IP address 192.168.1.1 to pass. system-view [DeviceB] interface ethernet 1/2 [DeviceB-Ethernet1/2] user-bind ip-address 192.168.0.1 mac-address 0001-0203-0406 [DeviceB-Ethernet1/2] quit # Dynamic IP source guard entries are generated dynamically according to client entries on the DHCP snooping or DHCP relay agent device. They are suitable for scenarios where many hosts are in a LAN and DHCP is used to allocate IP addresses to the hosts. Once DHCP allocates an IP address to a client, IP source guard automatically adds the entry to allow the client to access the network. A person using an IP address not obtained through DHCP cannot access the network. Dynamic IPv6 source guard entries are obtained from client entries on the ND snooping device. Following is a dynamic entry configuration example (DHCP snooping must have been enabled.) # # Enable dynamic entry generation on Ethernet 1/1. [Device] interface ethernet 1/1 [Device-Ethernet1/1] ip check source ip-address mac-address [Device-Ethernet1/1] quit # Port security Port security is a MAC address-based network access control mechanism. It is an extension to IEEE 802.1X and MAC authentication. It prevents access from unauthorized devices by checking the source MAC address of inbound traffic and access to unauthorized devices by checking the destination MAC address of outbound traffic. With port security enabled, frames whose source MAC addresses cannot be learned by the device in a security mode are considered illegal. The events that users do not pass IEEE 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication are considered illegal. Upon detection of illegal frames or events, the device takes the predefined action automatically. While enhancing the system security, this reduces your maintenance burden greatly. The illegal packets include: • Packets whose source MAC addresses are not learned • Packets failing authentication 27