ZyXEL G-300 User Guide - Page 20
Profile, Threshold Controls, Fragmentation Threshold, RTS Threshold, RTS Threshold
 |
View all ZyXEL G-300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 20 highlights
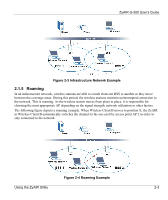
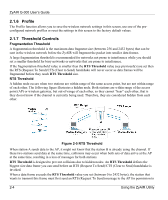
ZyAIR G-300 User's Guide 2.1.6 Profile The Profile function allows you to save the wireless network settings in this screen, use one of the preconfigured network profiles or reset the settings in this screen to the factory default values. 2.1.7 Threshold Controls Fragmentation Threshold A fragmentation threshold is the maximum data fragment size (between 256 and 2432 bytes) that can be sent in the wireless network before the ZyAIR will fragment the packet into smaller data frames. A large fragmentation threshold is recommended for networks not prone to interference while you should set a smaller threshold for busy networks or networks that are prone to interference. If the fragmentation threshold value is smaller than the RTS Threshold value (see previously) you set then the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented before they reach RTS Threshold size. RTS Threshold A hidden node occurs when two stations are within range of the same access point, but are not within range of each other. The following figure illustrates a hidden node. Both stations are within range of the access point (AP) or wireless gateway, but out-of-range of each other, so they cannot "hear" each other, that is they do not know if the channel is currently being used. Therefore, they are considered hidden from each other. Figure 2-5 RTS Threshold When station A sends data to the AP, it might not know that the station B is already using the channel. If these two stations send data at the same time, collisions may occur when both sets of data arrive at the AP at the same time, resulting in a loss of messages for both stations. RTS Threshold is designed to prevent collisions due to hidden nodes. An RTS Threshold defines the biggest size data frame you can send before an RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake is invoked. When a data frame exceeds the RTS Threshold value you set (between 0 to 2432 bytes), the station that wants to transmit this frame must first send an RTS (Request To Send) message to the AP for permission to 2-4 Using the ZyAIR Utility