ASRock ALiveDual-eSATA2 RAID Installation Guide - Page 6
NVIDIA RAID Installation Guide, 1 NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide, 1.1 Introduction to RAID - manual
 |
View all ASRock ALiveDual-eSATA2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
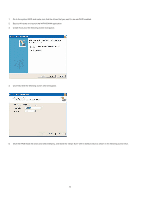
STEP 4: Install Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit OS on your system. Insert the Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit optical disk into the optical drive to boot your system, and follow the instruction to install Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit OS on your system. If you plan to install Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit on JMicron SATAII HDDs, when you see "Where do you want to install Windows?" page, please click the "Load Driver" button on the left on the bottom to load the JMicron RAID drivers from the SATAII driver diskette you just made. After that, please insert Windows Vista / Vista 64-bit optical disk into the optical drive again to continue the installation. 2. NVIDIA RAID Installation Guide If you insert two HDDs to NVIDIA SATA connectors and plan to configure RAID functions, please refer to NVIDIA RAID installation guide part, including NVIDIA BIOS RAID installation guide and NVIDIA Windows RAID installation guide. 2.1 NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide NVIDIA BIOS RAID Installation Guide is an instruction for you to configure RAID functions by using NVIDIA RAID Utility under BIOS environment. After you make a SATA driver diskette, press to enter BIOS setup to set the option to RAID mode by following the detailed instruction of the "User Manual" in our support CD or "Quick Installation Guide", you can start to use NVIDIA RAID Utility to configure RAID. This section includes examples of using NVRAID RAID Utility for creating RAID arrays (RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD). Please follow the instruction in this section to configure RAID functions.. 2.1.1 Introduction to RAID The term "RAID" stands for "Redundant Array of Independent Disks", which is a method combining two or more hard disk drives into one logical unit. For optimal performance, please install identical drives of the same model and capacity when creating a RAID set. RAID 0 (Data Striping) RAID 0 is called data striping that optimizes two identical hard disk drives to read and write data in parallel, interleaved stacks. It will improve data access and storage since it will double the data transfer rate of a single disk alone while the two hard disks perform the same work as a single drive but at a sustained data transfer rate. WARNING!! Although RAID 0 function can improve the access performance, it does not provide any fault tolerance. Hot-Plug any HDDs of the RAID 0 Disk will cause data damage or data loss. RAID 1 (Data Mirroring) RAID 1 is called data mirroring that copies and maintains an identical image of data from one drive to a second drive. It provides data protection and increases fault tolerance to the entire system since the disk array management software will direct all applications to the surviving drive as it contains a complete copy of the data in the other drive if one drive fails. JBOD (Spanning) A spanning disk array is equal to the sum of all drives. Spanning stores data onto a drive until it is full then proceeds to store files onto the next 6