ASRock ALiveDual-eSATA2 RAID Installation Guide - Page 9
Serial ATA, Array List - review
 |
View all ASRock ALiveDual-eSATA2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
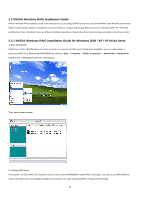
After assigning your RAID array disks, press to save your changes of RAID array disks. Depending on the platform used, the system can have one or more channels. In a typical system there is usually one adapter and multiple channels, and each channel has a slave and a master. The adapter / channel / master / slave status of each hard disk is given in the Loc (location) columns of the Free Disks and Array Disks lists. For example: 1 . 0 . M 1: Channel - Typically, channel 0 is used for Parallel ATA drives while channel 1 is used for Serial ATA drives. 0: Controller M: M means Master, S means Slave Serial ATA 1 . 0 . M Channel 1, controller 0, Master 1 . 1 . M Channel 1, controller 1, Master Finally, the Array List window appears, where you can review the RAID arrays that you have set up. Healthy NVIDIA STRIPING 74.53G 9