Belkin F5D8001 User Manual - Page 22
Bit WEP, Bit Encryption, Encryption Keys
 |
View all Belkin F5D8001 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
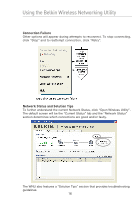
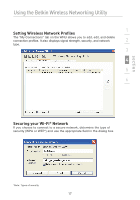
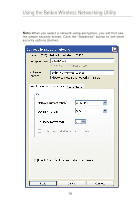
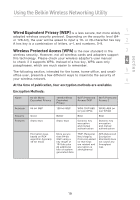
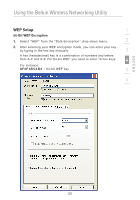
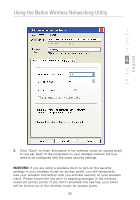
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility WEP WEP is a common protocol that adds security to all Wi-Fi-compliant wireless products. WEP gives wireless networks the equivalent level of privacy protection as a comparable wired network. 64-Bit WEP 64-bit WEP was first introduced with 64-bit encryption, which includes a key length of 40 bits plus 24 additional bits of system-generated data (64 bits total). Some hardware manufacturers refer to 64-bit as 40-bit encryption. Shortly after the technology was introduced, researchers found that 64-bit encryption was too easy to decode. 128-Bit Encryption As a result of 64-bit WEP's potential security weaknesses, a more secure method of 128-bit encryption was developed. 128bit encryption includes a key length of 104 bits plus 24 additional bits of system-generated data (128 bits total). Some hardware manufacturers refer to 128-bit as 104-bit encryption. Most of the new wireless equipment in the market today supports both 64bit WEP and 128-bit WEP encryption, but you might have older equipment that only supports 64-bit WEP. All Belkin wireless products will support both 64-bit WEP and 128-bit encryption. Encryption Keys After selecting either the 64-bit WEP or 128-bit encryption mode, it is critical that you generate an encryption key. If the encryption key is not consistent throughout the entire wireless network, your wireless networking devices will be unable to communicate with one another. You can enter your key by typing in the hex key. A hex (hexadecimal) key is a combination of numbers and letters from A-F and 0-9. For 64bit WEP, you need to enter 10 hex keys. For 128-bit WEP, you need to enter 26 hex keys. For instance: AF 0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key C3 03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key Write down the hex WEP key from your wireless router (or access point) and enter it manually into the hex WEP key table in your Card's configuration screen. 20