Cisco 7906G Administration Guide - Page 63
Process Step and Purpose, Related Topics, The Cisco IP Phone has non-volatile Flash memory
 |
UPC - 882658089343
View all Cisco 7906G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
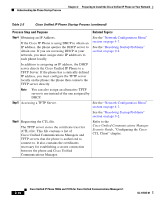
Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco Unified IP Phone on Your Network Understanding the Phone Startup Process Table 2-3 Cisco Unified IP Phone Startup Process Process Step and Purpose Related Topics Step 1 Obtaining Power from the Switch. If a phone is not using external power, the switch provides in-line power through the Ethernet cable attached to the phone. See the "Providing Power to the Cisco Unified IP Phones 7906G and 7911G" section on page 2-4. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. Step 2 The Cisco IP Phone has non-volatile Flash memory See the "Resolving Startup Problems" in which it stores firmware images and section on page 9-2. user-defined preferences. At startup, the phone runs a bootstrap loader that loads a phone image stored in Flash memory. Using this image, the phone initializes its software and hardware. Step 3 Configuring VLAN. See the "Network Configuration Menu" If the Cisco IP Phone is connected to a Cisco section on page 4-7. switch, the switch next informs the phone of the See the "Resolving Startup Problems" voice VLAN defined on the switch port. The phone section on page 9-2. needs to know its VLAN membership before it can proceed with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) request for an IP address. If a third-party switch is used and VLANs are configured, the VLAN on the phone must be manually configured. OL-14585-01 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7906G and 7911G for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.1 2-9