Cisco 7906G Administration Guide - Page 64
Cisco Unified Communications Managers and, Accessing a TFTP Server.
 |
UPC - 882658089343
View all Cisco 7906G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
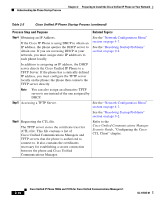
Understanding the Phone Startup Process Chapter 2 Preparing to Install the Cisco Unified IP Phone on Your Network Table 2-3 Cisco Unified IP Phone Startup Process (continued) Process Step and Purpose Related Topics Step 4 Obtaining an IP Address. If the Cisco IP Phone is using DHCP to obtain an IP address, the phone queries the DHCP server to obtain one. If you are not using DHCP in your network, you must assign static IP addresses to each phone locally. See the "Network Configuration Menu" section on page 4-7. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. In addition to assigning an IP address, the DHCP server directs the Cisco Unified IP Phone to a TFTP Server. If the phone has a statically defined IP address, you must configure the TFTP server locally on the phone; the phone then contacts the TFTP server directly. Note You can also assign an alternative TFTP server to use instead of the one assigned by DHCP. Step 5 Accessing a TFTP Server. See the "Network Configuration Menu" section on page 4-7. See the "Resolving Startup Problems" section on page 9-2. Step 6 Requesting the CTL file. The TFTP server stores the certificate trust list (CTL) file. This file contains a list of Cisco Unified Communications Managers and TFTP servers that the phone is authorized to connect to. It also contains the certificates necessary for establishing a secure connection between the phone and Cisco Unified Communications Manager. Refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security Guide, "Configuring the Cisco CTL Client" chapter. 2-10 Cisco Unified IP Phone 7906G and 7911G for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.1 OL-14585-01