Dell PowerConnect W-Series FIPS Dell PowerConnect W-600 Controller Series Secu - Page 22
Authentication Mechanisms, Unauthenticated Services, User Service
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect W-Series FIPS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
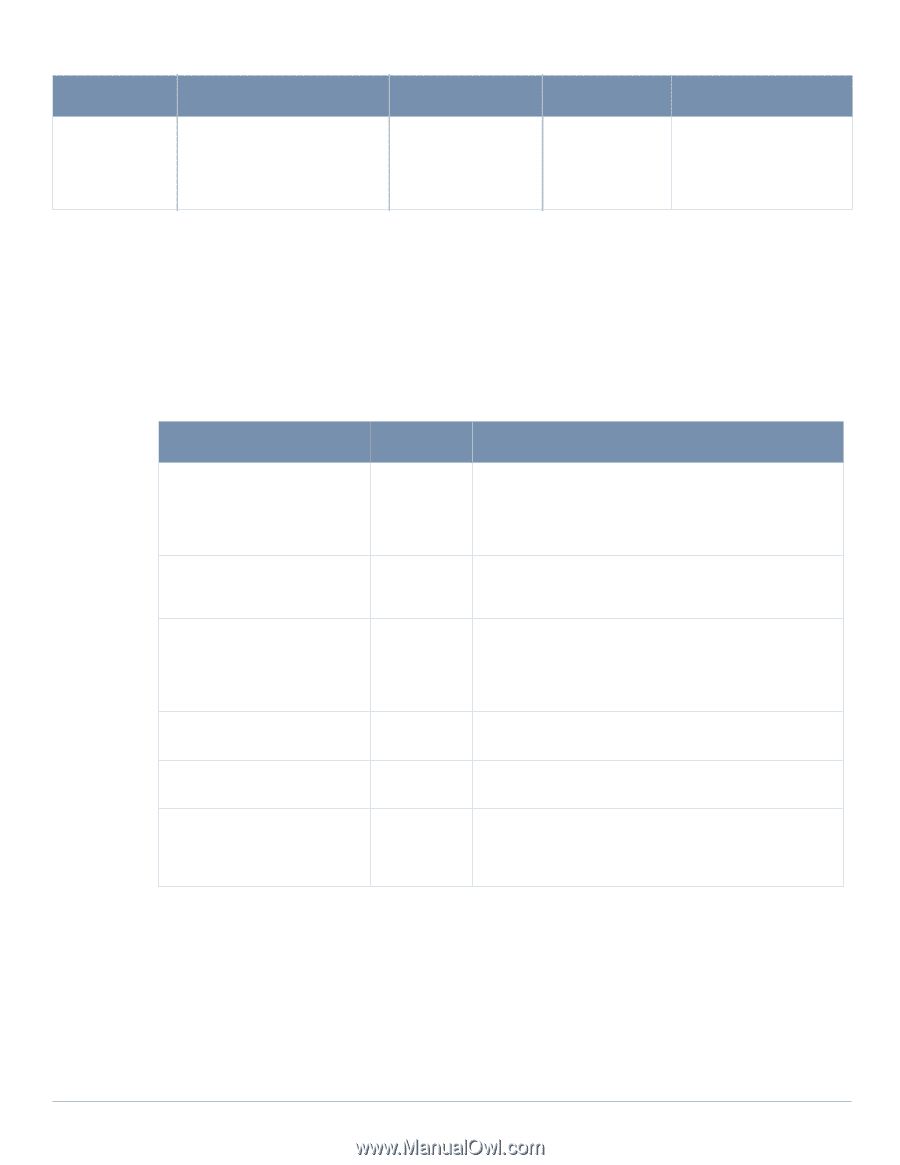
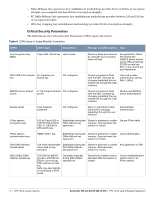
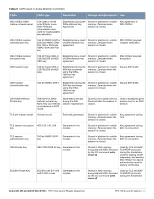
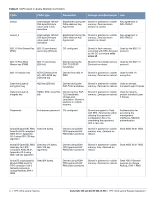
Table 4 User Service Service Description Data link (Layer 2) Encryption Access the module's Layer 2 encrypted tunnel services to secure network trafficData link encryption inputs, commands and data Input Output CSP Access Data link encryption Data link Data link encryption AES inputs, commands and encryption, status, key (read) data and data Authentication Mechanisms The Aruba Mobility Controller supports role-based authentication. Role-based authentication is performed before the Crypto Officer enters privileged mode using admin password via Web Interface or SSH or by entering enable command and password in console. Role-based authentication is also performed for User authentication. This includes password and RSA/ECDSA-based authentication mechanisms. The strength of each authentication mechanism is described below. Table 5 Estimated Strength of Authentication Mechanisms Authentication Type Role Strength Password-based authentication (CLI and Web Interface) Crypto Officer Passwords are required to be at least six characters long. Numeric, alphabetic (upper and lowercase), and keyboard and extended characters can be used, which gives a total of 95 characters to choose from. Therefore, the number of potential six-character passwords is 956 (735091890625). RSA-based authentication (IKEv1/IKEv2) User RSA signing and verification is used to authenticate to the module during IKEv1/IKEv2. This mechanism is as strong as the RSA algorithm using a 1024 or 2048 bit key pair. Pre-shared key-based authentication (IKEv1/IKEv2) User Pre-shared keys must be at least six characters long and up to 64 bytes long. Even if only uppercase letters were used without repetition for a six character pre-shared key, the probability of randomly guessing the correct sequence is one in 165,765,600. Pre-shared key based authentication (802.11i) User 1024 and 2048 bit RSA keys correspond to effective strength of 280 and 2112 respectively. EAP-TLS authentication User 1024 and 2048 bit RSA keys correspond to effective strength of 280 and 2112 respectively. ECDSA-based authentication (IKEv1/IKEv2) User ECDSA signing and verification is used to authenticate to the module during IKEv1/IKEv2. Both P-256 and P-384 keys are supported. ECDSA P-256 provides 128 bits of equivalent security, and P-384 provides 192 bits of equivalent security. Unauthenticated Services The Aruba Mobility Controller can perform SNMP management, VLAN, bridging, firewall, routing, and forwarding functionality without authentication. These services do not involve any cryptographic processing. Additional unauthenticated services include performance of the power-on self test and system status indication via LEDs. 20 | FIPS 140-2 Level 2 Features Aruba 620, 650 and Dell W-620, W-650 | FIPS 140-2 Level 2 Release Supplement