HP 6120XG HP ProCurve Series 6120 Blade Switches IPv6 Configuration Guide - Page 63
Loopback Address, The Unspecified Address
 |
View all HP 6120XG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
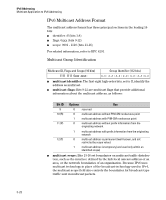
IPv6 Addressing Loopback Address ■ RFC 3306: Unicast-Prefix-based IPv6 Multicast Addresses ■ RFC 3956: Embedding the Rendezvous Point (RP) Address in an IPv6 Multicast Address ■ RFC 3177: IAB/IESG Recommendations on IPv6 Address Allocations to Sites ■ RFC 4007: IPv6 Scoped Address Architecture ■ RFC 4291: IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture ■ "Internet Protocol Version 6 Multicast Addresses" (at www.iana.org) Loopback Address The IPv6 loopback address is a link-local unicast address that enables a device to send traffic to itself for self-testing purposes. The loopback address does not have a physical interface assignment. If an IPv6 packet destined for the loopback address is received on a switch interface, it must be dropped. The IPv6 loopback address is never used as the source IPv6 address for any packet that is sent out of a device, and the switch drops any traffic it receives with a loopback address destination. An example use case is: ProCurve# ping6 ::1 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 is alive, time = 1 ms The Unspecified Address The "unspecified" address is defined as 0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0 (::/128, or just ::). It can be used, for example, as a temporary source address in multicast traffic sent by an interface that has not yet acquired its own address. The unspecified address cannot be statically configured on the switch, or used as a destination address. 3-24