HP 6840 HP Deskjet 6800 Printer series - (Macintosh OS 9) User's Guide - Page 23
Infrastructure networks, Mixed wired and wireless networks
 |
UPC - 829160429724
View all HP 6840 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
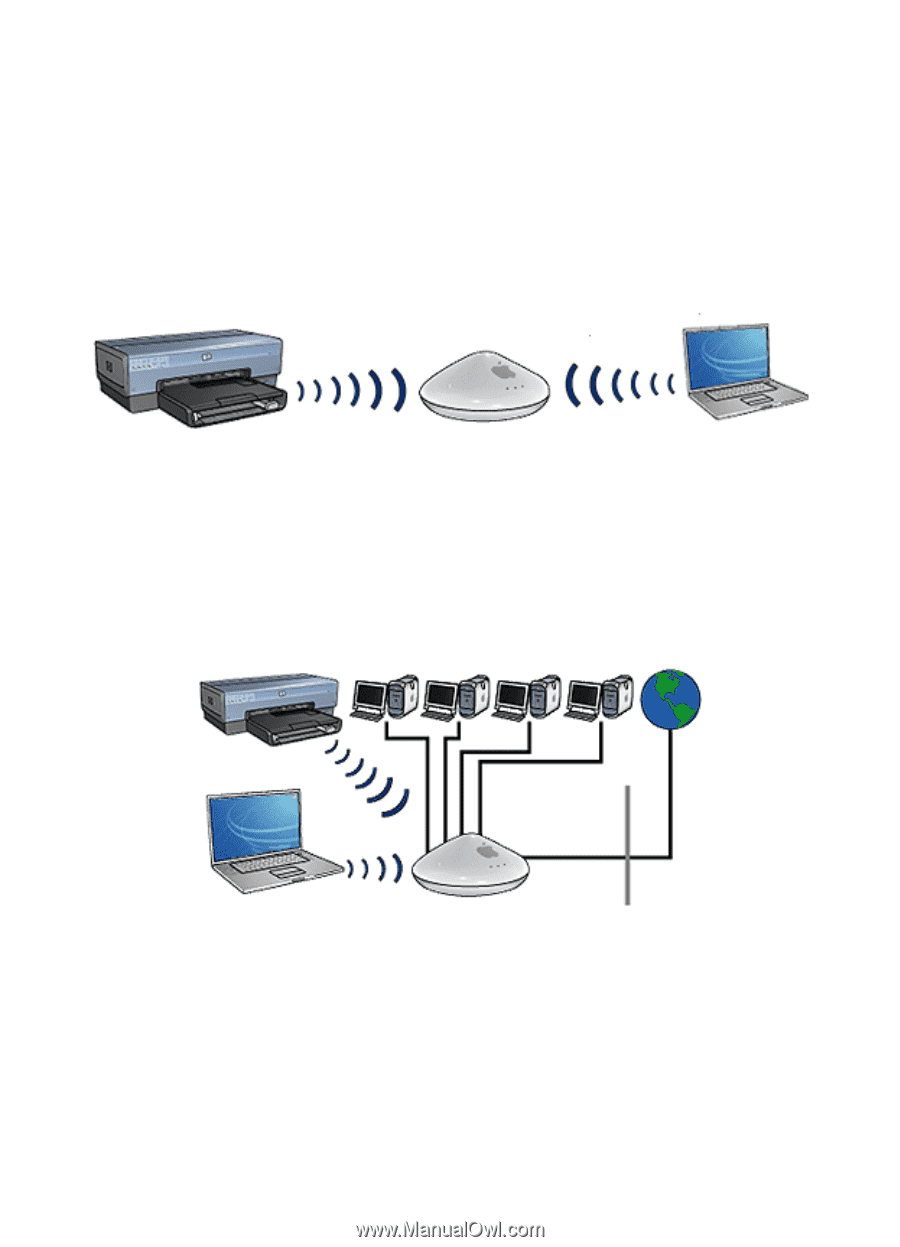
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer User's Guide Infrastructure networks On an infrastructure network, devices, such as computers and printers, communicate through a Wireless Access Point (WAP). WAPs commonly act as routers or gateways on small networks. For example, a simple infrastructure wireless network might consist of a laptop and a printer communicating through a WAP. Mixed wired and wireless networks Wireless devices often exist on a largely wired network. In this case, a WAP is connected to the main network by an Ethernet cable plugged into the WAP's WAN port. The WAP acts as the go-between for the wired devices and the wireless devices. The wired devices communicate with the WAP over the Ethernet cable, while the wireless devices communicate with the WAP over radio waves. For example, a mixed wired and wireless network may consist of the following: • Several desktop computers • A WAP connected to an Ethernet network • A printer connected wirelessly to the WAP In order to use the printer, a desktop PC sends a print job over the Ethernet cable to the WAP. The WAP then wirelessly transmits the print job to the printer. 23