Netgear FSM750S FSM750S Reference Manual - Page 48
of 121
 |
View all Netgear FSM750S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
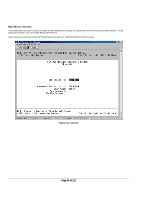
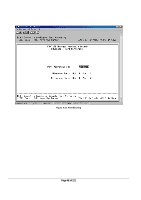
Main Menu> Advanced Menu There are 8 sub-menus here. o Port Mirroring o Port Trunking o Traffic Prioritization o VLANS o Spanning Tree o MAC o Multimedia Support o SNMP The Advanced page allows professional users to operate more complicated features of the device, which include VLAN, Spanning Tree, Port Trunking, Multimedia support (IGMP), traffic prioritization, SNMP, and port mirroring. These features are powerful and can degrade or damage a network's performance if improperly used. o Port Mirroring: Users can designate a port for monitoring traffic from one or more other ports or of a single VLAN configured on the switch. The switch monitors the network activity by copying all traffic from the specified monitoring sources to the designated monitoring port, to which a network analyzer can be attached. o Port Trunking: a feature that allows multiple links between switches to work as one virtual link (aggregate link). Trunks can be defined for similar port types only. For example, a 10/100 port cannot form a Port Trunk with a gigabit port. For 10/100 ports, trunks can only be formed within the same bank. A bank is a set of eight ports. Up to four trunks can be operating at the same time. Toggle the ports to the correct trunk number to set up a trunk. After clicking Apply, the trunk will be enabled. Spanning Tree will treat trunked ports as a single virtual port. o Multimedia Support (IGMP): The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an Internet protocol that provides a way for network devices to report multicast group membership to adjacent routers. o Traffic Prioritization (CoS): Class of Service (CoS), also referred to as Quality of Service (QoS), is a way of managing traffic in a network, by treating different types of traffic with different levels of service priority. Higher priority traffic gets faster treatment during times of switch congestion. o VLANs: A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a means to electronically separate ports on the same switch from a single broadcast domain into separate broadcast domains. By using VLAN, users can group by logical function instead of physical location. There are 64 VLAN supported on this switch. o Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ensures that only one path at a time is active between any two network nodes. There are maybe more than two physical path between any two nodes for redundant paths; STP ensures only one physical path is active and the others are blocked. STP will prevent an inadvertent loop in a network, which can disable your network due to a "Broadcast storm", the result of a broadcast message traveling through the loop again and again. o MAC: MAC address table Main Menu> Advanced Menu> Port Mirroring This menu option allows you to enable the Port Mirroring capability (see Figure 6-13). You need to specify both the Source and Monitor port. The Monitor port will show a copy of every packet that arrives and departs at the Source port. Page 47 of 121