Netgear FSM750S FSM750S Reference Manual - Page 94
of 121
 |
View all Netgear FSM750S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
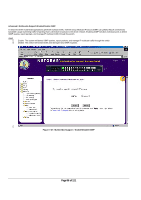
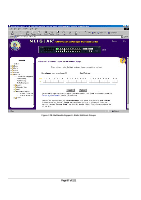
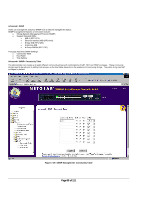
Advanced> Spanning Tree > Port Settings For the Port Settings options, you can specify Spanning Tree parameters for each port. The Spanning Tree parameters include port priority, path cost, and Fastlink. Table 7-1. STP Port Setting Parameters Parameters Range Description Prty (Priority) 0-255 STP bases on this to determine the port to use for forwarding. The port with the lowest number has the highest priority. Cost 1-65535 The switch uses this to determine which port is the forwarding port. All other factors equal, the path with the lowest cost to the root bridge will be the active path. Fastlink in STP mode When a port running the standard STP is connected, it will go through the STP negotiation (listening -> learning -> forwarding or blocking) before it will be fully available. If a client is trying to access a server through the switch running the STP negotiation, it will not be able to connect to it immediately. This can be a problem for some networks. Fastlink mode solves this problem by setting the port directly to forwarding mode, thus allowing any server access request to be forwarded. Fastlink mode can cause temporary loops in your network, but the STP will eliminate them. Fastlink is best used on end node ports, i.e. ports connected to PCs or servers, to avoid network loops. Figure 7-24: Spanning Tree: Port Settings Page 93 of 121