TRENDnet TEW-303PI Manual - Page 40
Supplicant: Wireless Network PC Card - drivers
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-303PI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
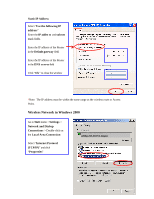
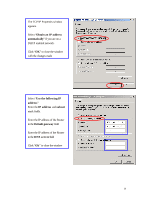
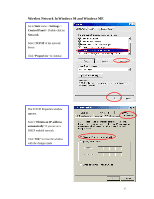
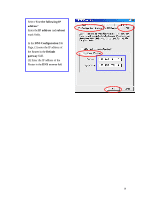
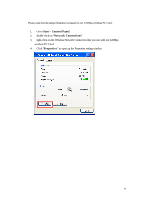
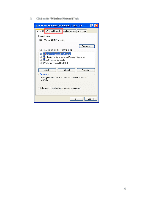
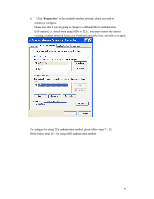
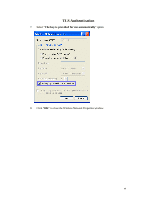
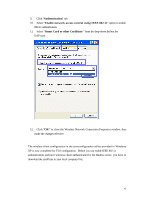
have access to the Internet/Intranet. In 802.1x authentication infrastructure, each of these wireless clients would have to be authenticated by the Radius server, which would grant the authorized client and notified the Access Point to open up a communication port to be used for the granted client. There are 2 Extensive Authentication Protocol (EAP) methods supported: (1) MD5 and (2) TLS. MD5 authentication is simply a validation of existing user account and password that is stored in the server with what are keyed in by the user. Therefore, wireless client user will be prompted for account/password validation every time when he/she is trying to get connected. TLS authentication is a more complicated authentication, which involves using certificate that is issued by the Radius server, for authentication. TLS authentication is a more secure authentication, since not only the Radius server authenticates the wireless client, but also the client can validate the Radius server by the certificate that it issues. The authentication request from wireless clients and reply by the Radius Server and Access Point process can be briefed as follows: 1. The client sends an EAP start message to the Access Point 2. The Access Point replies with an EAP Request ID message 3. The client sends its Network Access Identifier (NAI) - its user name - to the Access Point in an EAP Respond message. 4. The Access Point forwards the NAI to the RADIUS server with a RADIUS Access Request message. 5. The RADIUS server responds to the client with its digital certificate. 6. The client validates the digital certificate, and replies its own digital certificate to the RADIUS server. 7. The RADIUS server validates client's digital certificate. 8. The client and RADIUS server derive encryption keys. 9. The RADIUS server sends the access point a RADIUS ACCEPT message, including the client's WEP key. 10. The Access Point sends the client an EAP Success message along with the broadcast key and key length, all encrypted with the client's WEP key. Supplicant: Wireless Network PC Card Here is the setup for the Wireless Network PC Card under Windows XP, which is the only Operating System that our driver supports for 802.1x. Microsoft is planning on supporting 802.1x security in all common Windows Operating System including Win98SE/ME/2000 by releasing Service Pack in 2003. 40