ZyXEL NBG-419N v2 User Guide - Page 103
Encryption, 3.1.4
 |
View all ZyXEL NBG-419N v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 103 highlights
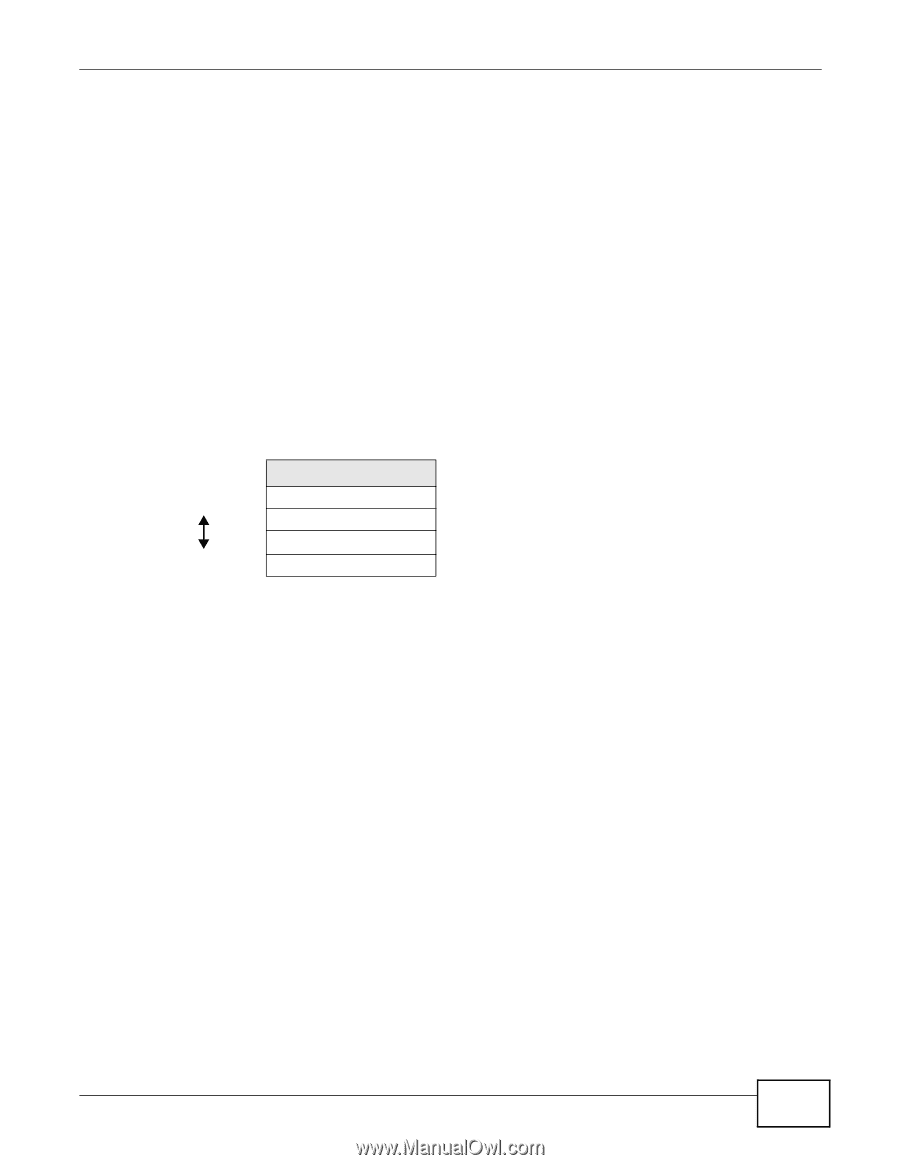
Chapter 12 Wireless LAN 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. To get the MAC address for each wireless client, see the appropriate User's Guide or other documentation. You can use the MAC address filter to tell the AP which wireless clients are allowed or not allowed to use the wireless network. If a wireless client is allowed to use the wireless network, it still has to have the correct settings (SSID, channel, and security). If a wireless client is not allowed to use the wireless network, it does not matter if it has the correct settings. This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the MAC address of an authorized wireless client. Then, they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network. 12.3.1.3 Encryption Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot understand the message. The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of user authentication. Table 41 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication NO AUTHENTICATION Weakest No Security WEP WPA-PSK Strongest WPA2-PSK Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every wireless client in the wireless network supports. Suppose the wireless network has two wireless clients. Device A only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP and WPA-PSK. Therefore, you should set up WEP in the wireless network. Note: It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK or stronger encryption. IEEE 802.1x and WEP encryption are better than none at all, but it is still possible for unauthorized devices to figure out the original information pretty quickly. When you select WPA2-PSK in your Router, you can also select an option (WPA Compatible) to support WPA as well. In this case, if some wireless clients support WPA and some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK (depending on the type of wireless network login) and select the WPA Compatible option in the Router. Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless network. The longer the key, the stronger the encryption. Every wireless client in the wireless network must have the same key. 12.3.1.4 WPS WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi Alliance. WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to configure security settings manually. Depending on the devices in your network, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in its configuration utility) or enter a PIN (Personal Identification Number) in the devices. Then, they connect and set up a secure network by themselves. See how to set up a secure wireless network using WPS in the Section 11.3 on page 87. NBG-419N v2 User's Guide 103