ZyXEL VFG6005 User Guide - Page 135
Using Configuration Files
 |
View all ZyXEL VFG6005 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 135 highlights
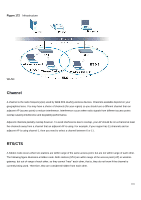
6 Click the Activate button to apply the changes. The following screen displays. Click Yes to save the changes in all screens. Figure 164 Red Hat 9.0: KDE: Network Configuration: Activate 7 After the network card restart process is complete, make sure the Status is Active in the Network Configuration screen. Using Configuration Files Follow the steps below to edit the network configuration files and set your computer IP address. 1 Assuming that you have only one network card on the computer, locate the ifconfig-eth0 configuration file (where eth0 is the name of the Ethernet card). Open the configuration file with any plain text editor. • If you have a dynamic IP address, enter dhcp in the BOOTPROTO= field. The following figure shows an example. Figure 165 Red Hat 9.0: Dynamic IP Address Setting in ifconfig-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=dhcp USERCTL=no PEERDNS=yes TYPE=Ethernet • If you have a static IP address, enter static in the BOOTPROTO= field. Type IPADDR= followed by the IP address (in dotted decimal notation) and type NETMASK= followed by the subnet mask. The following example shows an example where the static IP address is 192.168.10.10 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. Figure 166 Red Hat 9.0: Static IP Address Setting in ifconfig-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR=192.168.10.10 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 126