Compaq ProLiant 1000 Configuration and Tuning of Sybase System 11 for NetWare - Page 17
Separate Sequential and Random I/O's, Layout of Tables and Files
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
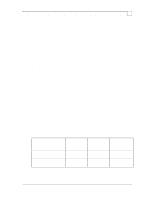
Configuration and Tuning of Sybase System 11 for NetWare on Compaq Servers Page 13 • Sequential I/O's are isolated to a controller volume, separate from volumes with random I/O's. This means sequential I/O volume should be alone on a controller or on one port of the controller. • Random I/O's are balanced across all drives allocated to data and indexes. • Physical disk I/O limits are not exceeded. Separate Sequential and Random I/O's In order to achieve maximum performance on data files being accessed sequentially, the disk(s) need to be dedicated to this purpose. Of primary importance are the Sybase transaction log files, which are accessed in a sequential, write-only fashion. Other partitions with little I/O activity can share the disk(s) with the transaction logs, such as the OS partition. In typical multi-user database systems, data access is random. This data should be spread out over as many physical disks as necessary to achieve random I/O rates that do not exceed recommendations. This is best achieved by using the disk striping available with the Compaq SMART SCSI Array Controller and SMART-2 SCSI Array Controller. Spreading out the disk requests among many disks allows a high degree of parallelism to occur on accesses. Using the Compaq SMART or SMART-2 SCSI Array Controller ensures that the load will be balanced equally across the disks. For more information on optimizing array configurations refer to the Compaq TechNote, Configuring Compaq RAID Technology for Database Servers. Layout of Tables and Files In order to improve performance where disk I/O is a problem, keep in mind the following. • Transaction log access is 100% sequential I/O and needs to be isolated if possible. Speed of the log is essential to the performance of the system. If possible, these drives should be fault tolerant, either mirrored or distributed data guarding. Hardware fault tolerance provides the maximum performance and reliability. See the Compaq TechNote Configuring Compaq RAID Technology for Database Servers. • Data file access is usually random and needs to be spread across as many drives as necessary. By increasing the number of physical drives, greater I/O rates can be achieved. Using a striped array will assure that the I/O's are well distributed. Use the following guidelines when monitoring and optimizing the drive subsystem. You should not have more I/O requests (disk transfers) per second per disk drive than the values in the following table. Sequential Writes (Transaction Log) Random Reads/Writes (Database Access) 1.0GB drives (Max I/Os per Second per Drive) ≈150 2.1GB drives (Max I/Os per Second per Drive) ≈160 4.3GB drives (Max I/Os per Second per Drive) ≈180 ≈30-40 ≈50 ≈55-60 NOTE: With the Array Accelerator enabled, you may actually see substantially higher I/O per second per drive rates than suggested above. This increase is due to the Array Accelerator write posting some of these I/Os. In the Compaq Database Performance labs we have actually © 1996 Compaq Computer Corporation, All Rights Reserved Doc No 140A/0896