HP Pavilion g4-2000 HP Pavilion g4 Notebook PC - Maintenance and Service Guide - Page 92
Creating the recovery media, Creating system restore points, What you need to know
 |
View all HP Pavilion g4-2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 92 highlights
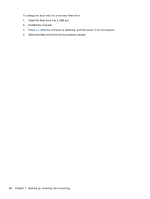
Creating the recovery media 1. Select Start and type recovery in the search field. Select Recovery Manager from the list. Allow the action to continue, if prompted. 2. Click Recovery Media Creation. 3. Follow the on-screen instructions to continue. To recover, see Recovering the original system using HP Recovery Manager on page 86 Creating system restore points A system restore point is a snapshot of certain hard drive contents saved by Windows System Restore at a specific time. A restore point contains information such as registry settings that Windows uses. Restoring to a previous restore point allows you to reverse changes that have been made to the system since the restore point was created. Restoring to an earlier system restore point does not affect data files saved or emails created since the last restore point, but it does affect software you may have installed. For example, if you download a photo from a digital camera and then restore the computer to the state it was on the previous day, the photo remains on the computer. However, if you install photo viewing software and then restore your computer to the state it was on the previous day, the software will be uninstalled, and you won't be able to use it. What you need to know ● If you restore to a restore point and then change your mind, you can undo the restoration. ● You should create system restore points: ◦ Before you add or change software or hardware ◦ Periodically, whenever the computer is running normally ● System Restore also saves shadow copies of files that have been changed since the last restore point was created. For more information about using shadow copies to restore, see Help and Support. Creating a system restore point 1. Select Start > Control Panel > System and Security > System. 2. In the left pane, click System Protection. 3. Click the System Protection tab. 4. Click Create, and follow the on-screen instructions. To restore, see Restoring to a previous system restore point on page 86. Backing up system and personal information Your computer stores information that is important to you, such as files, emails, and photos, and you will want to keep that information even if you download a virus or the system stops working properly. How completely you are able to recover your files depends on how recent your backup is. As you add new software and data files, you should create backups on a regular basis. 84 Chapter 7 Backing up, restoring, and recovering