HP ProLiant BL660c Configuring Arrays on HP Smart Array Controllers Reference - Page 98
Raid 1+0 (raid 10
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
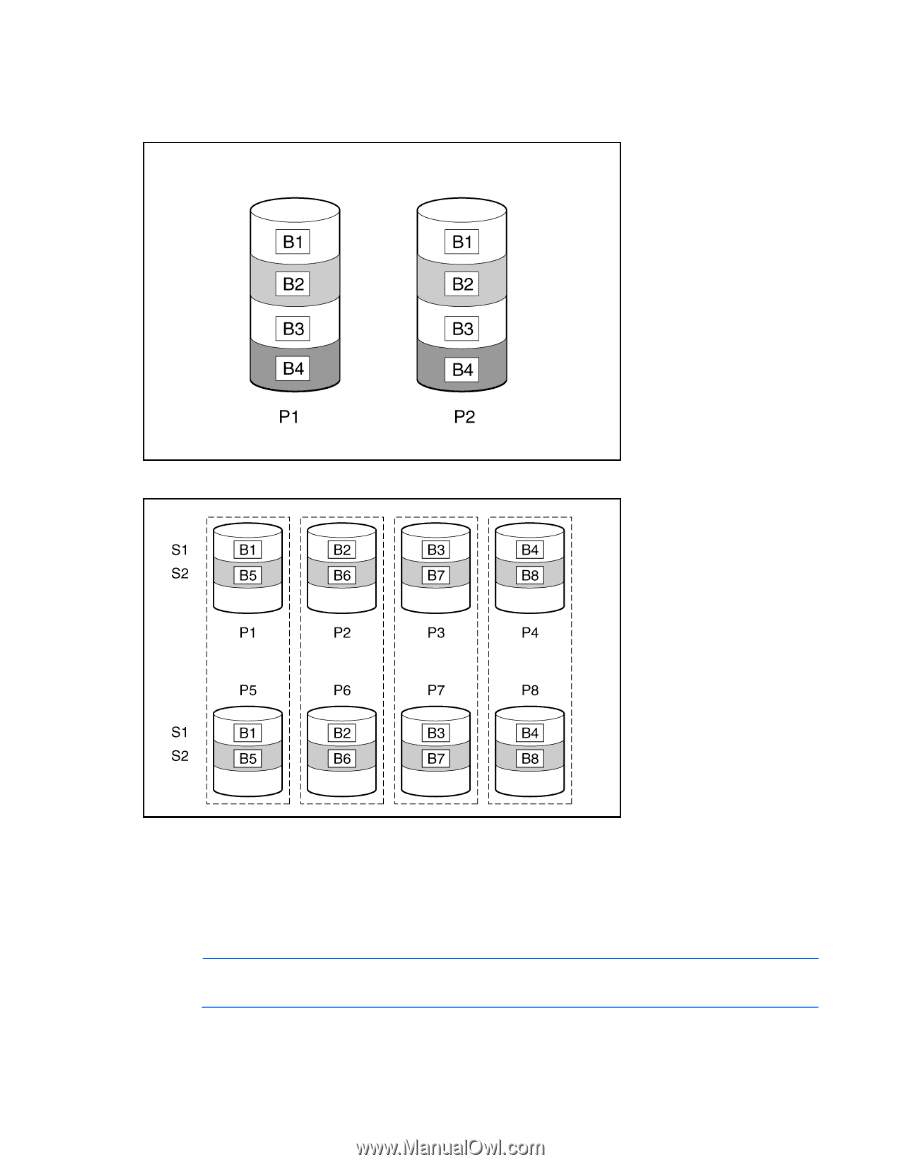
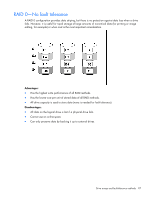
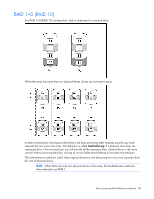
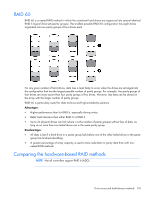
RAID 1+0 (RAID 10) In a RAID 1+0 (RAID 10) configuration, data is duplicated to a second drive. When the array has more than two physical drives, drives are mirrored in pairs. In each mirrored pair, the physical drive that is not busy answering other requests answers any read requests that are sent to the array. This behavior is called load balancing. If a physical drive fails, the remaining drive in the mirrored pair can still provide all the necessary data. Several drives in the array can fail without incurring data loss, as long as no two failed drives belong to the same mirrored pair. This fault-tolerance method is useful when high performance and data protection are more important than the cost of physical drives. NOTE: When there are only two physical drives in the array, this fault-tolerance method is often referred to as RAID 1. Drive arrays and fault-tolerance methods 98