Linksys BEFW11S4 User Guide - Page 21
The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing, Setup Tab - Routing Table - version 1
 |
UPC - 745883549948
View all Linksys BEFW11S4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
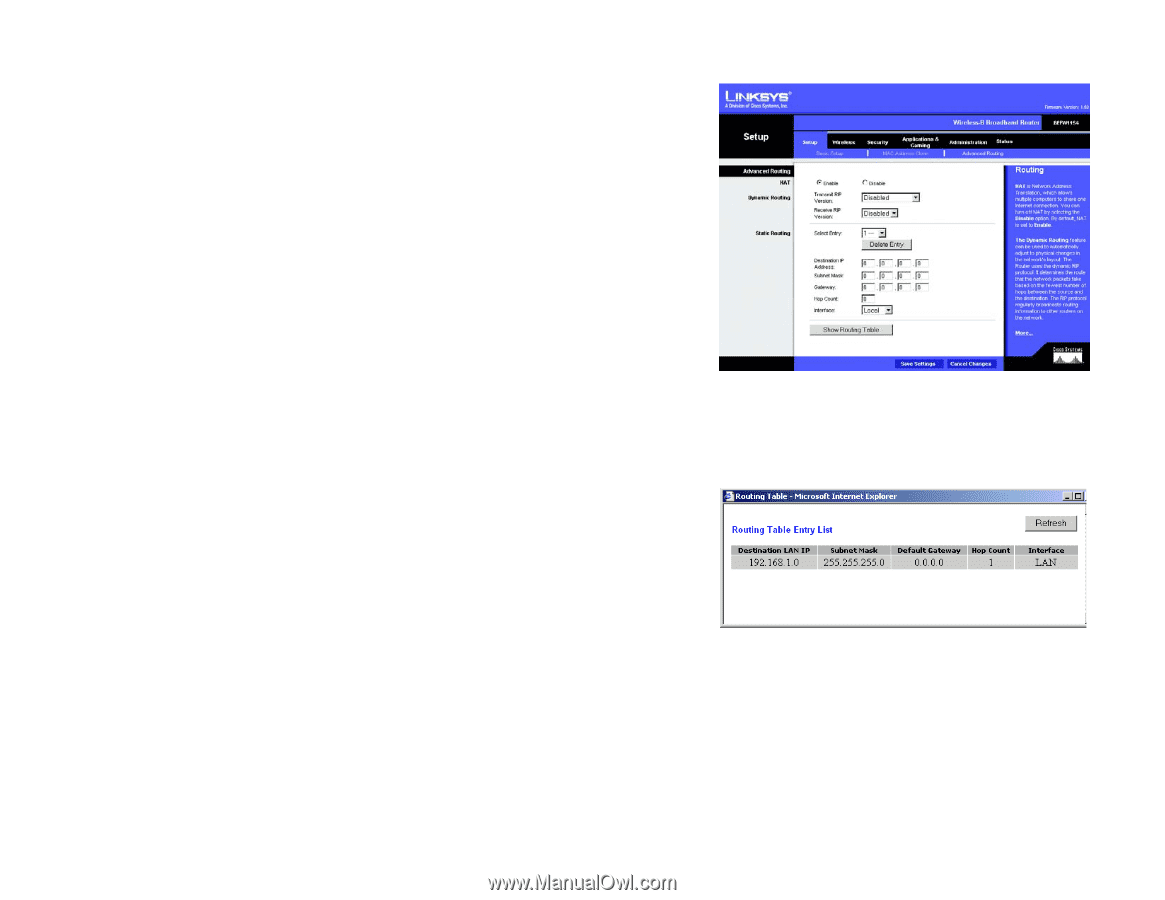
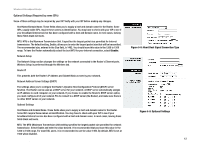
Wireless-B Broadband Router The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing This tab is used to set up the Router's advanced functions. Dynamic Routing will automatically adjust how packets travel on your network. Static Routing sets up a fixed route to another network destination. NAT. Network Address Translation (NAT) technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a different IP address for the Internet. To enable the NAT function, click Enable. Dynamic Routing. With Dynamic Routing you can enable the Gateway to automatically adjust to physical changes in the network's layout. The Gateway, using the RIP protocol, determines the network packets' route based on the fewest number of hops between the source and the destination. The RIP protocol regularly broadcasts routing information to other Gateways on the network. To enable RIP, click Enabled. To disable RIP, click Disabled. • Transmit RIP Version. To transmit RIP messages, select the protocol you want: RIP1, RIP1-Compatible, or RIP2. If you don't want to transmit RIP messages, select None. • Receive RIP Version. To receive RIP messages, select the protocol you want: RIP1 or RIP2. If you don't want to receive RIP messages, select None. Static Routing. To set up a static route between the Router and another network, select a number from the Select Entry drop-down list. (A static route is a pre-determined pathway that network information must travel to reach a specific host or network.) Enter the information described below to set up a new static route. (Clicking the Delete Entry will delete a static route.) Destination IP Address. The Destination LAN IP is the address of the remote network or host to which you want to assign a static route. Subnet Mask. The Subnet Mask determines which portion of a Destination LAN IP address is the network portion, and which portion is the host portion. Gateway. This is the IP address of the gateway device that allows for contact between the Router and the remote network or host. Hop Count. This determines the maximum number of steps between network nodes that data packets will travel. A node is any router in the path to the remote network. Interface. This interface tells you whether the Destination IP Address is on the Local (Ethernet and wireless networks) or the Internet. Figure 5-11: Setup Tab - Advanced Routing Figure 5-12: Setup Tab - Routing Table Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-B Broadband Router 15 The Setup Tab - Advanced Routing