Asus P3V133 P3V133 User Manual - Page 57
DRAM to run at 100MHz. Configuration options: [Auto] [FSB] [2/3 FSB]
 |
View all Asus P3V133 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
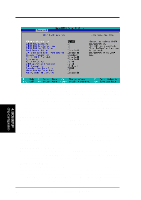
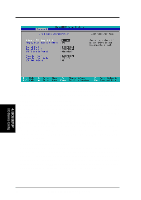
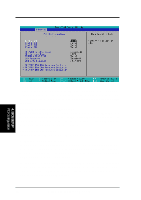
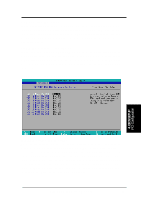
4. BIOS SETUP CPU-DRAM Back-Back Transaction [Disabled] Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] Delayed Transaction [Enabled] When [Enabled], this frees the PCI Bus when the CPU is accessing 8-bit ISA cards that normally consume about 50-60 PCI Clocks without PCI delayed transaction. Select [Disabled] for ISA cards that are not PCI 2.1 compliant. Configuration options: [Enabled] [Disabled] PCI to DRAM Prefetch [Disabled] Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] Byte Merge [Disabled] To optimize the data transfer on PCI, this merges a sequence of individual memory writes (bytes or words) into a single 32-bit block of data. However, byte merging may only be done when the bytes within a data phase are in a prefetchable address range. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] MD to HD Delay [Auto] Configuration options: [Auto] [0 T] [1 T] DRAM Operating Frequency [Auto] By default, the BIOS automatically detects the DRAM type and allows the DRAM to run at its optimal frequency. You may also set this in conjunction with the Front Side Bus (FSB)/external frequency. For example, when you set the external frequency to 133MHz, selecting [2/3 FSB] allows your DRAM to run at 100MHz. Configuration options: [Auto] [FSB] [2/3 FSB] AGP Capability [2X Mode] This motherboard supports the AGP 2x interface, which transfers video data at 533MB/s. Since AGP 2x is backward-compatible, you may leave the default [2X Mode] on no matter you are using an AGP 1x or 2x video card. When set to [1X Mode], the AGP interface will only provide a peak data throughput of 266MB/s even if you are using an AGP 2x card. Configuration options: [1X Mode] [2X Mode] Graphics Aperture Size [64MB] This feature allows you to select the size of mapped memory for AGP graphic data. Configuration options: [4MB] [8MB] [16MB] [32MB] [64MB] [128MB] [256MB] Video Memory Cache Mode [UC] USWC (uncacheable, speculative write combining) is a new cache technology for the video memory of the processor. It can greatly improve the display speed by caching the display data. You must set this to UC (uncacheable) if your display card cannot support this feature; otherwise your system may not boot. Configuration options: [UC] [USWC] Memory Hole At 15M-16M [Disabled] This field allows you to reserve an address space for ISA expansion cards that require it. Configuration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] 4. BIOS SETUP Chip Configuration ASUS P3V133 User's Manual 57