D-Link DXS-1100-10TS User Manual - Page 69
From Port / To Port, State, Guard Root, Link Type, Shared, Port Fast, Network, Disabled, TCN Filter
 |
View all D-Link DXS-1100-10TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
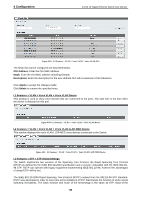
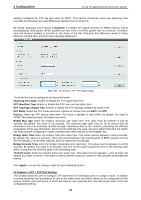
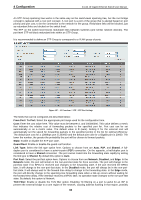
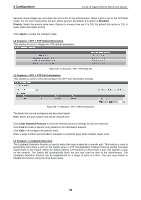
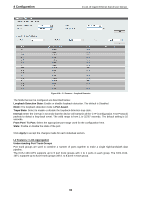
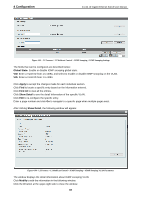
4 Configuration D-Link 10 Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge concept is replaced with a root port concept. A root port is a port of the group that is elected based on port priority and port cost, to be the connection to the network for the group. Redundant links will be blocked, just as redundant links are blocked on the switch level. The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices). The port level STP will block redundant links within an STP Group. It is recommended to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports. Figure 4.87 - L2 Functions > STP > STP Port Settings The fields that can be configured are described below: From Port / To Port: Select the appropriate port range used for the configuration here. Cost: Enter the cost value here. This value must be between 1 and 200000000. This value defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto). Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency. The default port cost for a 100Mbps port is 200000 and the default port cost for a Gigabit port is 20000. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets. State: Enable or disable the STP port state. Guard Root: Enable or disable the guard root function. Link Type: Select the link type option here. Options to choose from are Auto, P2P, and Shared. A fullduplex port is considered to have a point-to-point (P2P) connection. On the opposite, a half-duplex port is considered to have a Shared connection .The port cannot transit into the forwarding state rapidly by setting the link type to Shared. By default this option is Auto. Port Fast: Select the port fast option here. Options to choose from are Network, Disabled, and Edge. In the Network mode, the port will remain in the non-port-fast state for three seconds. The port will change to the port-fast state if no BPDU is received and changes to the forwarding state. If the port received the BPDU later, it will change to the non-port-fast state. In the Disabled mode, the port will always be in the non-portfast state. It will always wait for the forward-time delay to change to the forwarding state. In the Edge mode, the port will directly change to the spanning-tree forwarding state when a link-up occurs without waiting for the forward-time delay. If the interface receives a BPDU later, its operation state changes to the non-port-fast state. By default, this option is Network. TCN Filter: Enable or disable the TCN filter option. Enabling TC filtering on a port is useful for an ISP to prevent the external bridge to a core region of the network, causing address flushing in that region, possibly 62