Dell EqualLogic PS6210S EqualLogic Auto-Snapshot Manager/Microsoft Edition Ver - Page 82
Smart Copy Schedules for Hyper-V, Hyper-V Restore Operations, Restore a VM In-Place
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 82 highlights
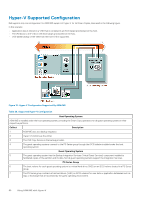
Smart Copy Schedules for Hyper-V The procedure for scheduling Smart Copies of virtual machines is the same as the general operations described in General ASM/ME Operations, except that if a VM is offline, it is still copied in its offline state. The shutdown state affects the Smart Copy as follows: • When a VM shuts down cleanly, the Smart Copy is application-consistent. • When a VM has crashed or is powered off without a shutdown, the Smart Copy is crash-consistent. Schedules fail if you remove a VM permanently without updating any schedules or scheduled collections of which that VM was previously a member. Hyper-V Restore Operations ASM/ME supports the following types of data restoration for virtual machines described in the following table. Table 30. Restore Operations for Hyper-V Operation In-Place Restore Selective Restore Restore As New Menu Option Restore All Restore selected VMs Restore As New Restore operations are always disruptive regardless of the type of guest O/S that is installed in the VM. The restore operation has the following sequence: • The Hyper-V management console displays a message confirming that it is performing the restore operation. • The VM is taken offline and is deleted by the VSS writer. If you are running a remote desktop to the guest, the remote desktop session is terminated. • ASM/ME restores the VM files. • When the restore operation completes, the VM is registered with the Hyper-V service, which adds it to the list of VMs in the Hyper-V management console. If the VM was running before the restore operation was initiated, ASM/ME restarts the VM. • If the VM crashed and you initiated a restore operation to recover it, the VM is left in the powered-off state by the ASM/ME restore operation. Restore a VM In-Place With an in-place restore operation, you can restore all VMs in the Smart Copy. This type of operation restores all data on all PS Series volumes used by all VMs included in the Smart Copy. For in-place restore operations, all VMs on the volumes being restored experience a service interruption. 1. Right-click the VM Smart Copy in the ASM/ME GUI and select Restore All. A confirmation dialog box opens. 2. Click Yes. Selectively Restore a VM With a selective restore operation, you specify one or more VMs you want restored. The default size of a VHD file is 127GB. Such large file sizes require adequate time to copy and restore. Therefore, consider reducing the volume size to the optimum required for the application and user space. 1. Right-click the VM Smart Copy in the ASM/ME GUI and select Restore selected VMs. The Select Virtual Machines dialog box opens. 2. Select the virtual machine you are restoring and click Restore. When the restore operation is finished, a message displays, stating that the operation completed successfully. Restore a VM as New The Restore as New operation is available for snapshots and clones. This operation creates a new VM that is local and non-clustered. The VM is created locally on the current node and uses the default VM settings and an amount of user-specified RAM that uses the original VM's .vhd files. Restore as New currently supports up to four .vhd files during a restore. 1. Expand the Smart Copies node, right-click the relevant VM, and select Restore As New. 82 Using ASM/ME with Hyper-V