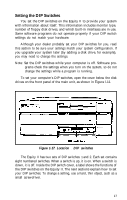
Epson Equity II User Manual - Page 27
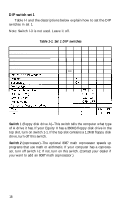
Table 1-2. Set 2 DIP switches, Switch, parity, Switch 7 internal serial interface--To, internal serial
 |
View all Epson Equity II manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 27 highlights
Table 1-2. Set 2 DIP switches Switch 5 (parity checking,)-Parity checking is the method your computer uses to detect any errors in RAM. If you enable parity checking and the computer detects an error in memory, an error message displays. For maximum protection, turn off switch 2-5 to enable parity checking. To disable parity checking, turn on this switch. Switch 7 (internal serial interface)--To use two serial devices (usually a serial printer or modem), you need to designate the built-in serial interface as either primary or secondary. In MS-DOS, you would then refer to it as COM1 or COM2 respectively. To use the built-in interface as the primary device, turn off switch 2-7. If you have not installed an extra serial interface, the built-in interface is the primary device regardless of how you set this switch. If you have installed an optional serial interface, you can use the built-in port as the secondary device if you turn on switch 2-7. You can then select any peripheral connected to the optional port as the primary device. Most option cards which contain serial interfaces have jumper connectors which you must set to tell MS-DOS whether you are using the port as COM1 or COM2. If you use the built-in interface as the primary device, you must set the jumper on the optional interface to make it COM2. If you accidentally set both to act as the primary device, you will not damage the computer, but you will get unpredictable results from both interfaces. Switch 8 (internal serial interface)--If you connected a peripheral to the built-in serial port on the back panel, turn off switch 2-8 to enable this port. If you do not want to use the built-in serial port, turn on switch 2-8 to disable it. For example, you need to disable the built-in port if you use an optional port as COM1 and a modem as COM2; MS-DOS can only recognize two serial devices. 20