HP OmniBook XE2-DE HP OmniBook XE2 Notebook PC - Setup Guide - Page 34
every hour is a good idea. Short, frequent breaks are more beneficial than longer less
 |
View all HP OmniBook XE2-DE manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 34 highlights
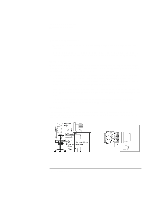
Using the OmniBook PC Working in Comfort be flush with the front edge of the keyboard. Other items, such as your telephone or notepad, also should be considered. • Monitor: Place your monitor so that the top of the screen is at, or slightly below, eye level (up to 15 degrees). • Head: Do not tilt your head forward by more than 15 degrees, and try not to turn your head toward the side. • Back: While sitting at your work surface, make sure your back is supported by the chair's backrest in an erect position or angled slightly backwards. • Arms: Make sure your arms and elbows are relaxed and loose, with your upper arm perpendicular to the floor or slightly forward. Keep your forearms and hands approximately parallel with the floor with elbows bent between 70 and 115 degrees. Keep your elbows close to your sides (less than 20 degrees away from your body). • Legs: Your thighs should be horizontal or angled slightly downward. Your lower legs should be near a right angle to your thighs. Make sure there is sufficient room under the work surface for your legs. • Feet: If after adjusting your chair you cannot rest your feet comfortably on the floor, use a footrest, preferably one that can be adjusted in height and angle. Overall • Look away from the screen from time to time to help reduce eyestrain. Focus on distant objects briefly, and blink periodically to lubricate your eyes. You also should have your eyes checked on a regular basis and ensure your eyeglass prescription is suitable for working on a monitor screen. • Remember to occasionally shift position and move your body. Keeping your body in one position for long periods is unnatural and stressful. When prolonged work is required, take frequent short breaks. As a rule of thumb, a five- or ten-minute break every hour is a good idea. Short, frequent breaks are more beneficial than longer less frequent breaks. Data show that people who work for long periods of time without a break may be more prone to injury. • Changing tasks frequently will help prevent muscle stiffness. Examples: alternating between keyboarding, reading, writing, filing, and moving around in your work environment, helps you maintain a relaxed posture. Occasionally stretch the muscles in your hands, arms, shoulders, neck, and back. You should stretch at least as often as you take brief task breaks-at least once every hour. • Discomfort may be alleviated by using alternative ergonomic designs and accessories such as ergonomically personalized chairs, palm rests, keyboard trays, alternative input devices, prescription eyeglasses, anti-glare screens, and more. Seek additional 34 Setup Guide