HP Vectra XU 6/XXX HP Vectra XU 6/XXX - Guide to Optimization Performance - Page 36
Out-of-order Execution, Speculative Execution
 |
View all HP Vectra XU 6/XXX manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
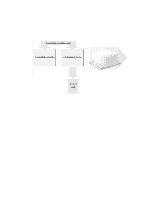
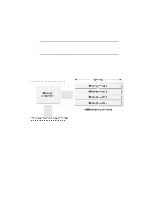
and addresses. The Pentium Pro provides five execution units, giving it increased flexibility for instruction execution. To ensure that the pipelines are used to their greatest efficiency, the Pentium Pro must keep its instruction units busy. For this reason, the Pentium Pro implements two additional features for instruction execution: out-of-order execution; and speculative execution. Out-of-order Execution When executing x86 family instructions, previous generations of processors had to be faithful to the order in which the instructions were received. This meant that if a particularly slow or complicated instruction was being executed, the processor was obliged to stall its pipeline until the instruction had completed. By breaking instructions down into micro-ops, the Pentium Pro is able to change the order in which it executes instructions.When a particular instruction requires longer than average to execute, the Pentium Pro will fetch and execute another instruction while waiting for the first instruction to complete. The status of the first instruction is stored in registers while the new instruction is executed, ensuring that no conflicts arise. This facility is called out-of-order execution, and ensures that the Pentium Pro's three pipelines are used to their greatest effect. Speculative Execution All programs contain branches. These are produced by conditional instructions which can change the thread of instruction execution. Depending on the conditions when a conditional instruction is executed, different instructions will be required next by the program. Like the Pentium processor, the Pentium Pro provides a branch prediction unit that can identify program branches and load their instructions into the level-one instruction cache memory. However, unlike the Pentium, the Pentium Pro is also able to execute these instructions in case they are needed. This feature is called speculative execution, and it can significantly reduce the time required for program branches.