HP Vectra XU 6/XXX HP Vectra XU 6/XXX - Guide to Optimization Performance - Page 37
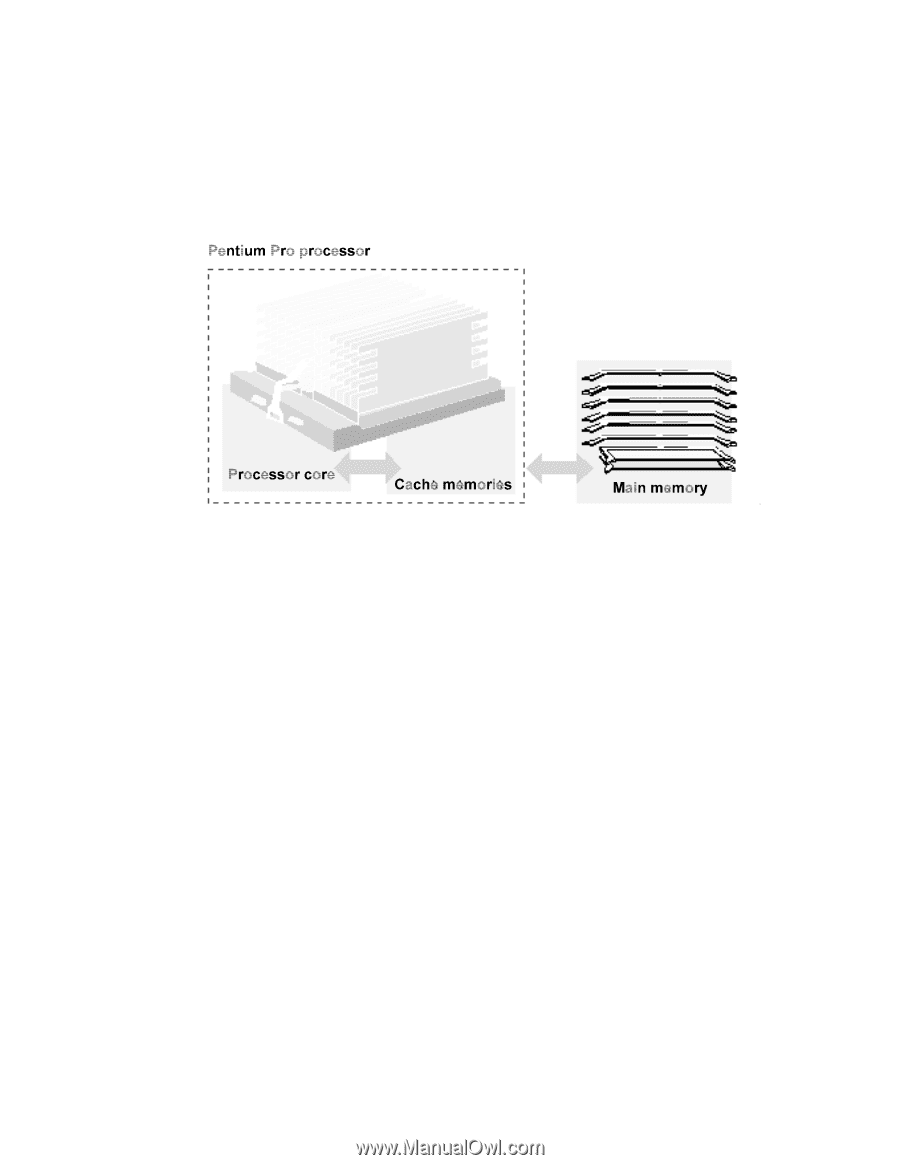
Integrated Cache Memory
 |
View all HP Vectra XU 6/XXX manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
INTEGRATED CACHE MEMORY Cache memories are used by processors to accelerate access times for frequently used data and instructions. A cache is located between the processor and main memory, and stores copies of the last data read or written by the processor. If the same data is requested again by the processor, it will be supplied from the cache at significantly reduced access time. Cache memory has a much smaller capacity than main memory and stores not only data, but also the memory addresses that correspond to the data. When the processor reads or writes data in memory, the address for that data is compared with the addresses stored in the cache. If a match is found, the cache registers a cache hit and the data will be read or written directly from or to the cache. If a match is not found, a cache miss occurs and the cycle will be passed to main memory with no time penalty. Two levels of Integrated Cache The Pentium Pro processor integrates three cache memories in the same package: an 8 KB level-one data cache; an 8 KB level-one instruction cache; and a 256 KB unified level-two cache. The cache level refers to the proximity of the cache to the processor's pipelines; the level-one caches are closer to the pipelines than the level-two cache. The caches are hierarchical, so that any data or instructions stored in level-one cache memories will also be stored in the level-two cache memory. Level-One Caches The Pentium Pro's two 8 KB level-one caches are similar to the level-one caches integrated in the Pentium processor. Both level-one caches use a two-way set-associative organization, meaning that they consist of two, separate logical banks of equal size (4 KB each). Level-Two Cache The Pentium Pro's 256 KB level-two cache stores both data and instructions. The level-two cache uses a four-way set-associative organization (four banks of 64 KB). Set-associative caches offer greater flexibility for storing data items that have similar memory addresses.