Intel BX80571E5300 Data Sheet - Page 13
Electrical Specifications - motherboard
 |
UPC - 735858204996
View all Intel BX80571E5300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
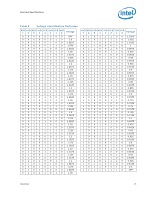
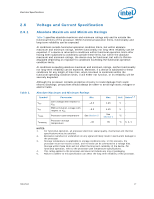
Electrical Specifications 2 Electrical Specifications 2.1 2.2 2.2.1 2.2.2 This chapter describes the electrical characteristics of the processor interfaces and signals. DC electrical characteristics are provided. Power and Ground Lands The processor has VCC (power), VTT, and VSS (ground) inputs for on-chip power distribution. All power lands must be connected to VCC, while all VSS lands must be connected to a system ground plane. The processor VCC lands must be supplied the voltage determined by the Voltage IDentification (VID) lands. The signals denoted as VTT provide termination for the front side bus and power to the I/O buffers. A separate supply must be implemented for these lands, that meets the VTT specifications outlined in Table 4. Decoupling Guidelines Due to its large number of transistors and high internal clock speeds, the processor is capable of generating large current swings. This may cause voltages on power planes to sag below their minimum specified values if bulk decoupling is not adequate. Larger bulk storage (CBULK), such as electrolytic or aluminum-polymer capacitors, supply current during longer lasting changes in current demand by the component, such as coming out of an idle condition. Similarly, they act as a storage well for current when entering an idle condition from a running condition. The motherboard must be designed to ensure that the voltage provided to the processor remains within the specifications listed in Table 4. Failure to do so can result in timing violations or reduced lifetime of the component. VCC Decoupling VCC regulator solutions need to provide sufficient decoupling capacitance to satisfy the processor voltage specifications. This includes bulk capacitance with low effective series resistance (ESR) to keep the voltage rail within specifications during large swings in load current. In addition, ceramic decoupling capacitors are required to filter high frequency content generated by the front side bus and processor activity. Consult the Voltage Regulator-Down (VRD) 11.0 Processor Power Delivery Design Guidelines For Desktop LGA775 Socket for further information. Contact your Intel field representative for additional information. VTT Decoupling Decoupling must be provided on the motherboard. Decoupling solutions must be sized to meet the expected load. To ensure compliance with the specifications, various factors associated with the power delivery solution must be considered including regulator type, power plane and trace sizing, and component placement. A conservative decoupling solution would consist of a combination of low ESR bulk capacitors and high frequency ceramic capacitors. Datasheet 13