LG VX10 User Guide - Page 6
Subject
 |
View all LG VX10 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
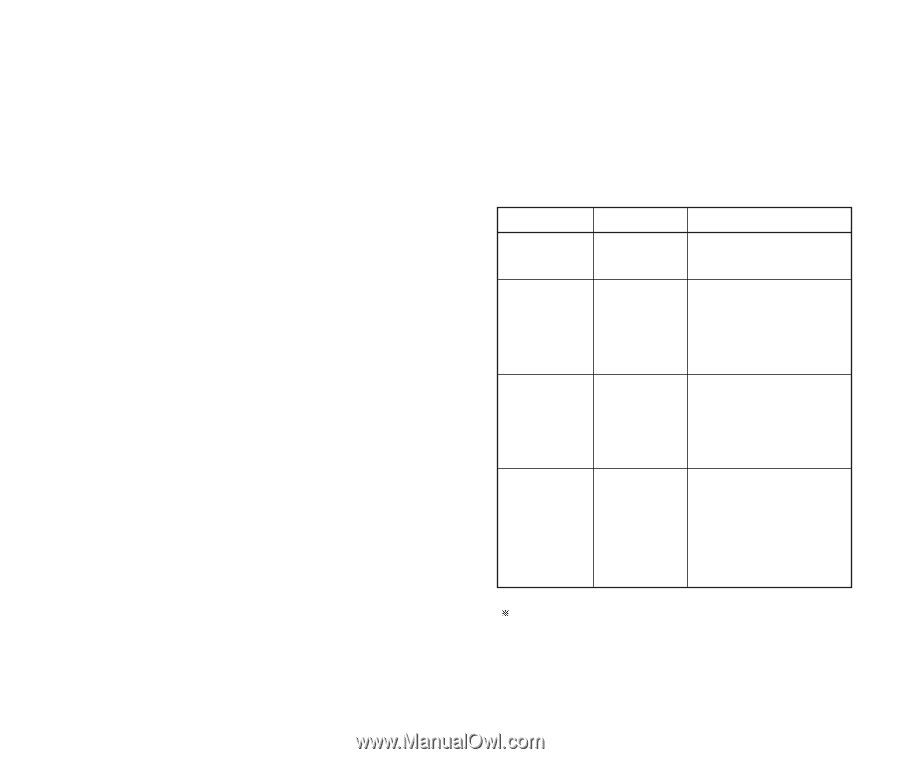
Subject The VX10 phone has been designed to operate on the latest digital mobile communication technology, Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA). This CDMA digital technology has greatly enhanced voice clarity and can provide a variety of advanced features. Currently, CDMA mobile communication technology has been commercially used in Cellular and Personal Communication Service (PCS). The difference between them is operating frequency spectrum. Cellular uses 800Mhz and PCS uses 1.9Ghz. The VX10 operates on both frequencies, this is called a dual-band phone. Also, the VX10 works on Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS). We call it a trimode phone. If one of the Cellular, PCS or AMPS base stations is located nearby, call fail rate of a tri-mode phone is less than a dual-mode phone or a single-mode phone. CDMA technology adopts DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum). DSSS enables the phone to keep communication from being crossed and to use one frequency channel by multiple users in the same specific area, resulting in a 10 fold increase in capacity when compared with the analog mode currently used. Soft/Softer Handoff, Hard Handoff, and Dynamic RF power Control technologies are combined into this phone to reduce call interruptions. 4 The Cellular and PCS CDMA networks consist of MSO (Mobile Switching Office), BSC (Base Station Controller), BTS (Base station Transmission System), and MS (Mobile Station). The following table lists some major CDMA Standards. CDMA Standard Designator Description TIA/EIA/IS-95-A Protocol between MS and BTS for Cellular & AMPS Basic air interface ANSI J-STD-008 Protocol between MS and BTS for PCS TIA/EIA/IS-634 MAS-BS Network TIA/EIA/IS/651 TIA/EIA/IS-41-C PCSC-RS Intersystem operations TIA/EIA/IS-124 Nom-signaling data comm. TIA/EIA/IS-96-B Speech CODEC Service TIA/EIA/IS-99 TIA/EIA/IS-637 Assign data and fax Short message service TIA/EIA/IS-657 Packet data TIA/EIA/IS-97 Cellular base station TIA/EIA/IS-98 Cellular mobile station Performance ANSI J-STD-018 PCS personal station ANSI J-STD-019 PCS base station TIA/EIA/IS-125 Speech CODEC TSB -74: Protocol between an IS-95A system and ANSI JSTD-008 1xRTT system receives subscribers in wireless section twice as much as IS-95. Its battery life is twice as long as IS-95. High-speed data transmission is also possible. 5