Linksys WRT54GS-FR User's Manual - Page 6
After going through Getting to Know the Wireless-G, - router manual
 |
UPC - 745883560028
View all Linksys WRT54GS-FR manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
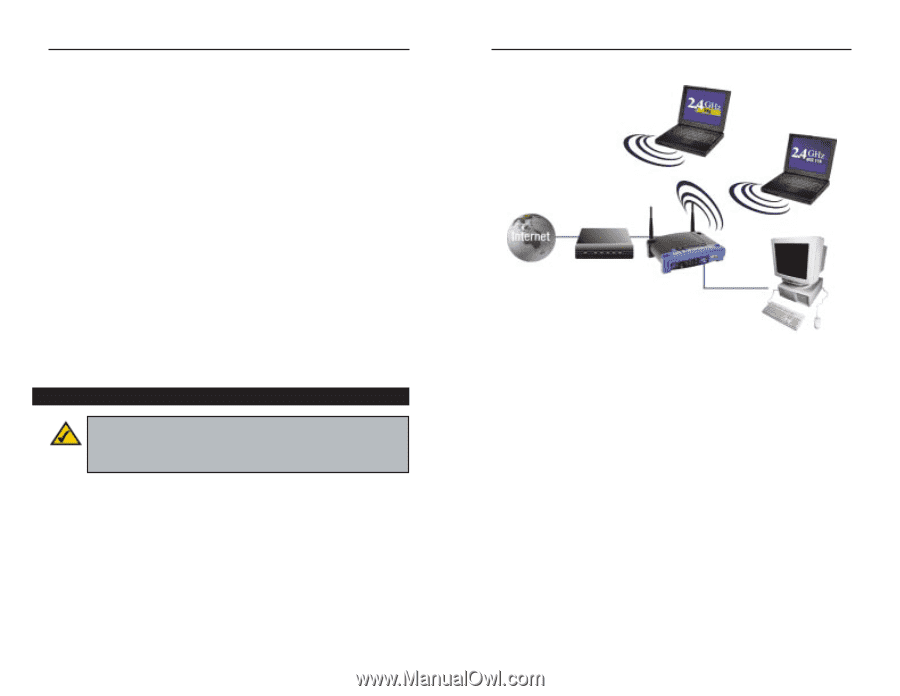
Instant Wireless® Series Dynamic IP Addresses A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network, such as PCs and print servers. These IP addresses are called "dynamic" because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or device. After a certain time period, they expire and may change. If a PC logs onto the network (or the Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the DHCP server will automatically assign it a new dynamic IP address. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Servers PCs and other network devices using dynamic IP addressing are assigned a new IP address by a DHCP server. The PC or network device obtaining an IP address is called the DHCP client. DHCP frees you from having to assign IP addresses manually every time a new user is added to your network. A DHCP server can either be a designated PC on the network or another network device, such as the Router. By default, the Router's DHCP Server function is enabled. If you already have a DHCP server running on your network, you must disable one of the two DHCP servers. If you run more than one DHCP server on your network, you will experience network errors, such as conflicting IP addresses. To disable DHCP on the Router, see the DHCP section in "Chapter 6: The Router's Web-based Utility." Router Setup Overview Note: You should always run the Setup CD-ROM to configure the Router for Internet access. If you wish to manually configure the Router, you may follow the instructions in the Quick Installation guide or this User Guide. This User Guide covers the steps for setting up a network with the Router (see Figure 1-1). After going through "Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Wireless-G Broadband Router," most users will only need to use the following chapters: • Chapter 3: Connect the Router This chapter instructs you on how to connect a cable or DSL modem to the Router and connect your PC(s) to the Router. 4 Wireless-G Broadband Router Notebook with Wireless-G Adapter Notebook with Wireless 802.11b Adapter Cable or DSL Modem Router PC with Ethernet Adapter Figure 1-1 • Chapter 4: Configure the PCs This chapter instructs you on how to configure your PCs to be DHCP clients, if you have previously set static IP addresses on your PCs. • Chapter 5: Configure the Router's Basic Settings This chapter explains how to configure the Router using your web browser and the Router's web-based utility. You will configure the Router for Internet access using the settings provided by your ISP. When you're finished with these basic steps, you will be ready to connect to the Internet. You can also modify the Router's settings further; for example, you can adjust security features and other settings to enable online gaming (see "Chapter 6: The Router's Web-based Utility"). 5