Onkyo HT-R540 Owner Manual - Page 23
Connecting Audio and Video Signals to the AV Receiver, Which Connections Should I Use? - support
 |
View all Onkyo HT-R540 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
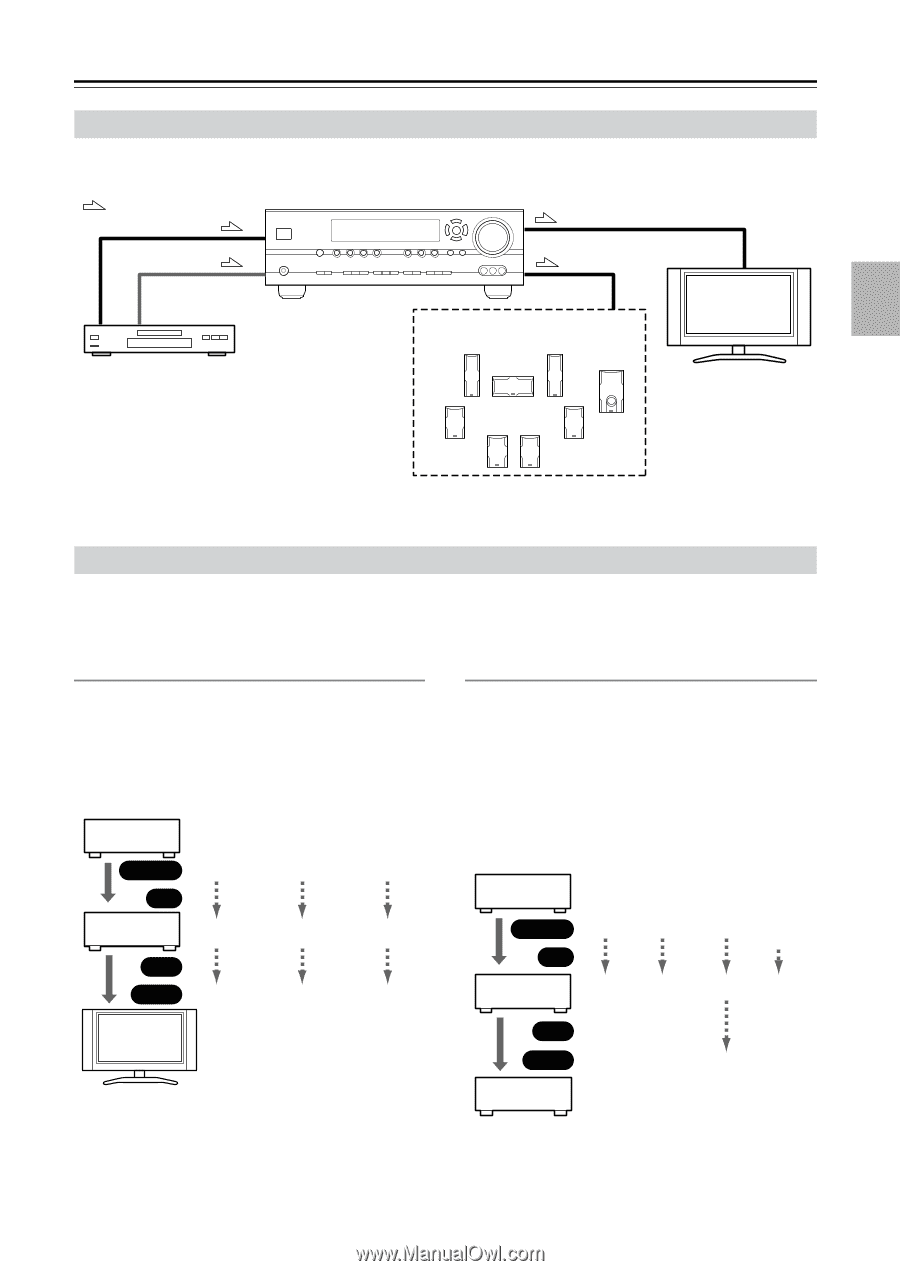
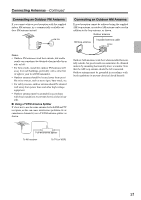
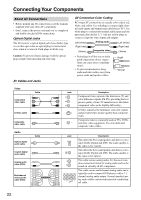
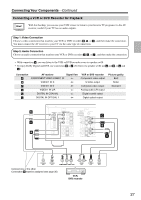
Connecting Your Components-Continued Connecting Audio and Video Signals to the AV Receiver By connecting both the audio and video outputs of your DVD player and other AV components to the AV receiver, you can switch the audio and video signals simultaneously simply by changing the input source on the AV receiver. : Signal Flow Video Video Audio Audio DVD player, etc. Speakers (see page 19 for hookup details) TV, projector, etc. Which Connections Should I Use? The AV receiver supports several connection formats for compatibility with a wide range of AV equipment. The format you choose will depend on the formats supported by your other components. Use the following sections as a guide. For video components, such as a DVD player, you must make an audio connection and a video connection. Video Connection Formats Audio Connection Formats When choosing a connection format, bear in mind that the AV receiver doesn't convert between formats, so only outputs of the same format as the input will output the signal. Video Signal Flow Chart DVD player, etc. Output IN Composite AV Receiver Composite OUT Input Composite S-Video S-Video S-Video Component Component Component When choosing a connection format, bear in mind that the AV receiver doesn't convert between formats. For example, audio signals connected to an OPTICAL or COAXIAL digital input are not output by the analog TAPE OUT, so if you want to record from, for example, your CD player, in addition to connecting it to a digital input, you must also connect it to the analog CD IN. Audio Signal Flow Chart CD player, etc. Output Optical Coaxial IN AV Receiver Optical Coaxial Analog Multichannel Analog Multichannel TV, projector, etc. OUT Input Cassette recorder, etc. Analog 23