Compaq ProLiant 1000 Compaq Backup and Recovery for Microsoft SQL Server 6.X - Page 52
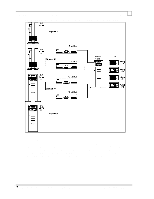
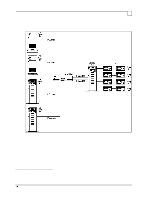
Each of these four systems is connected to a dedicated 10Base-T repeater
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
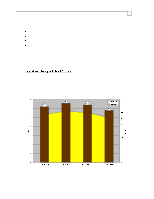
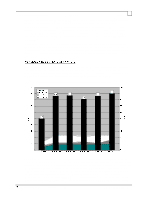
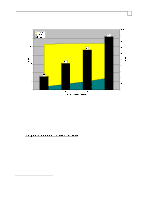
Compaq Backup and Recovery for Microsoft SQL Server 6.x Page 52 network utilization, it was never seen to exceed an average of 25%. The CPU usage at both the source and destination servers is also moderate, not exceeding 10% and 16% respectively. This lack of ability to saturate the 100 Mbit wire could be attributed to a combination of things, but is mostly due to idle time on the wire between successive transmissions. The sending node can only transmit a certain number of bytes across the network before it must pause and wait for an acknowledgment (ACK) from the receiving node72. Idle periods result in an overall sustained throughput that is much lower than the instantaneous transfer rate between the two nodes. The positive side is that enough bandwidth remains on the wire for other network tasks to complete without very much interruption. We now change to a concurrent, or parallel backup scheme, meaning that more than one database server is backed up at a time to a single storage server. This requires that the network layout be changed as well. Four database servers are placed on the network: two Proliant 5000 systems and two Proliant 2500 systems73. Each of these four systems is connected to a dedicated 10Base-T repeater (hub), and each repeater is connected to one of four network cards within the single storage server. The network layout is shown in Figure-1. This layout ensures that a dedicated 10 Mbit path is available from each database server to the storage server. 72 The number of bytes transmitted without receiving an ACK may be adjusted by varying the size of the TCP receive window, through use of a TCP/IP parameter in the Windows NT registry (called TcpWindowSize). The default size (with ethernet) is 8760, meaning that 6 frames of 1460 bytes each may be sent consecutively. A larger receive window may improve performance with high delay or high bandwidth networks, although we did not notice much difference in our environment. 73 See beginning of section for system specifics. Although the Proliant 5000 systems are more powerful than the Proliant 2500's, for the purposes of these tests they behave identically.