Sony MZ-NH900 Operating Instructions - Page 104
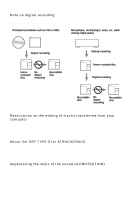
Difference between digital optical and analog line inputs
 |
View all Sony MZ-NH900 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
Difference between digital (optical) and analog (line) inputs The input jack of this recorder works as both digital and analog input jacks. Connect the recorder to a CD player or a cassette recorder using either digital (optical) input or analog (line) input. To record, see "Recording a disc right away!" (page 21) to record using digital (optical) input, and "Recording from a TV or radio (Analog Recording)" (page 37) to record using analog (line) input. Difference Digital (optical) input Analog (line) input Connectable Equipment with a digital (optical) output Equipment with an analog (line) source jack (CD player, DVD player, etc.) output jack (Casette deck, radio, record player, etc.) Usable cord Optical cable (with an optical or an optical-mini plug) (page 21) Line cable (with 2 phono plugs or a stereo-mini plug) (page 37) Signal from Digital the source Analog Even when a digital source (such as a CD) is connected, the signal sent to the recorder is analog. Track marks1) Marked (copied) automatically • at the same positions as the source (when the sound source is a CD or an MD). • after more than 2 seconds of no sound (page 100) or low-level segment (with a sound source other than a CD or an MD). • when the recorder is paused (3 seconds of no sound is encountered while synchro-recording) Marked automatically • after more than 2 seconds of no sound (page 100) or low-level segment. • when the recorder is paused while recording. Recorded sound level Same as the source. Can also be adjusted manually (Digital REC level control) ("Adjusting the recording level manually", page 38). Adjusted automatically. Can also be adjusted manually ("Adjusting the recording level manually", page 38). 1) You can erase unnecessary marks after recording. ("Combining tracks (Combine)", page 72). Note Track marks may be copied incorrectly: • when you record from some CD players or multi disc players using digital (optical) input. • when the source is in shuffle or program play mode while recording using digital (optical) input. In this case, play the source in normal play mode. • when programs with audio that is digitally broadcast (e.g., digital TV) are recorded through the digital (optical) input. 104