D-Link DGS-3208F Product Manual - Page 9
Features, Ports, Performance features
 |
UPC - 790069222092
View all D-Link DGS-3208F manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
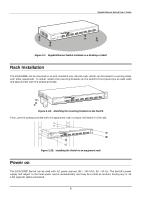
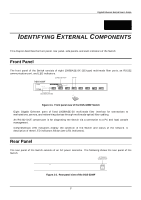
Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Guide segments. This allows the total network capacity to be multiplied, while still maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards. Switching LAN technology is a marked improvement over the previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by higher latencies. Routers have also been used to segment local area networks, but the cost of a router and the setup and maintenance required make routers relatively impractical. Today's switches are an ideal solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems. Features The DGS-3208F Gigabit Ethernet Switch was designed for easy installation and high performance in an environment where traffic on the network and the number of users increase continuously. Switch features include: Ports ♦ Eight 1000BASE-SX (SC-type fiber transceiver) Gigabit Ethernet ports. ♦ RS-232 DCE console port for diagnosing the Switch via a connection to a PC and console/out-of-band management. Performance features ♦ Store and forward switching scheme capability to support rate adaptation and protocol conversion. ♦ Full duplex to allow two communicating stations to transmit and receive at the same time. ♦ Data forwarding rate 1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed for 1000-Mbps speed. ♦ Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at 1,488,100 pps per port at 100% of wire- speed for 1000-Mbps speed. ♦ 12K active MAC address entry table per device with automatic learning and aging. ♦ 16 MB packet buffer per device. ♦ Supports broadcast storm rate filtering. ♦ Supports IGMP snooping. ♦ Supports port mirroring. ♦ Supports GVRP. ♦ Supports GMRP (802.1P). ♦ Supports 802.1P priority (tag mode). ♦ Supports static filtering (based on MAC Address) ♦ Supports port-based VLAN (overlapping VLANs are excluded). ♦ Supports IEEE 802.1Q VLAN. 2