Denon S-302 Owners Manual - English - Page 49
Windows Media DRM, About Wireless LAN
 |
UPC - 081757507882
View all Denon S-302 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
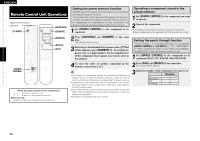
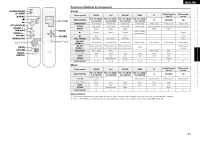
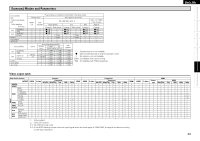
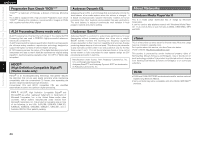
Getting Started Connections Setup Playback Remote Control Information Troubleshooting ENGLISH Windows Media DRM A copyright-protected technology developed by Microsoft. • Windows Vista and the Windows logo are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. • The PlaysForSure logo, Windows Media and the Windows logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. • Content providers are using the digital rights management technology for Windows Media contained in this device (WM-DRM) to protect the integrity of their content (Secure Content) so that their intellectual property, including copyright, in such content is not misappropriated. This device uses WM-DRM software to play Secure Content (WMDRM Software). If the security of the WM-DRM Software in this device has been compromised, owners of Secure Content (Secure Content Owners) may request that Microsoft revoke the WM-DRM Software's right to acquire new licenses to copy, display and/or play Secure Content. Revocation does not alter the WM-DRM Software's ability to play unprotected content. A list of revoked WM-DRM Software is sent to your device whenever you download a license for Secure Content from the Internet or from a PC. Microsoft may, in conjunction with such license, also download revocation list onto your device on behalf of Secure Content Owners. IEEE 802.11g This is another wireless LAN standard set by the 802 working group that establishes LAN technology standards at the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) of the United States, and is compatible with IEEE 802.11b. It also uses the 2.4 GHz band, but enables communications at a maximum speed of 54 Mbps. The value indicated above is the maximum theoretical value for the wireless LAN standard, and does not indicate the actual data transfer rate. Infrastructure Communications "Infrastructure Communications" refers to networks using wireless LAN access points. This function can be used to connect to the Internet or a wired LAN via a wireless LAN access point. Wireless LAN access points include wireless broadband routers. Ad-hoc Communications Signal transfer through wireless interconnection of computers is referred to as "ad hoc communications". With such ad hoc communications there is no connection to the Internet. Ad hoc communications are suited for establishing simple temporary networks. WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) This is a security standard established by the Wi-Fi Alliance. In addition to the conventional SSID (network name) and WEP key (network key), it also uses a user identification function and encrypting protocol for stronger security. WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) This is a new version of the WPA established by the Wi-Fi Alliance, compatible with more secure AES encryption. WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (Pre-shared Key) This is a simple authentication system for mutual authentication when a preset character string matches on the wireless LAN access point and client. Passphrase This refers to the code key used forWPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK authentication, a WPA authentication method. TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) This is a network key used for WPA. The encryption algorithm is RC4, the same as for WEP, but the security level is increased by changing the network key used for encryption for each packet. About Wireless LAN Wi-Fi® Wi-Fi Certification assures tested and proven interoperability by the Wi-Fi Alliance, a group certifying interoperability among wireless LAN devices. IEEE 802.11b This is one wireless LAN standard set by the 802 working group that establishes LAN technology standards at the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) of the United States. It uses the 2.4 GHz band usable freely without a radio frequency license (ISM band), enabling communications at a maximum speed of 11 Mbps. Network Names (SSID: Security Set Identifier) When forming wireless LAN networks, groups are formed to prevent interference, data theft, etc. This grouping is done by "SSID" or "Security Set Identifiers". For further security, a WEP key is set and signal transfer is not possible unless the SSID and WEP key match. WEP Key (Network Key) This is key information used for encrypting data when conducting data transfer. On the S-302, the same WEP key is used for data encryption and decryption, so the same WEP key must be set on both devices in order for communications to be established between them. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) This is a next generation standard encryption method replacing the current DES and 3DES, and because of its high security it is expected to be applied widely to wireless LANs in the future. It uses the "Rijndael" algorithm developed by two Belgian cryptographers to divide the data into blocks of fixed lengths and encrypt each block. It supports data lengths of 128, 192 and 256 bits and key lengths of 128, 192 and 256 bits as well, offering extremely high encryption security. The value indicated above is the maximum theoretical value for the wireless LAN standard, and does not indicate the actual data transfer rate. 45