HP 6840 HP Deskjet 6800 Printer series - (Windows) User's Guide - Page 45
Wired Ethernet networking - network setup
 |
UPC - 829160429724
View all HP 6840 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 45 highlights
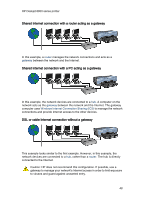
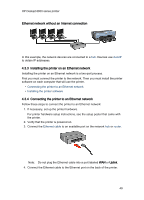
HP Deskjet 6800 series printer WEP key: A WEP key, or encryption key, is a sequence of alphanumeric characters or hexadecimal digits. After creating a WEP key, you must remember it or store it in a secure location. You may not be able to retrieve the WEP key if you lose it. A WEP key is either 64 or 128 bits long. The first 24 bits of the key are provided automatically. When creating the WEP key, the person creating the key provides the remaining bits (40 bits in the case of a 64-bit key, or 104 bits in the case of a 128-bit key). Wireless Access Point (WAP): A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a device through which devices (for example, computers and printers) on an infrastructure wireless network communicate with one another. A WAP is also called a base station. Wireless profile: A wireless profile is a collection of wireless network settings that applies to a particular wireless network. For example, a wireless LAN card can have one profile for a home network and another profile for an office network. When installing a device on a network, be sure to select the appropriate profile. WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) provides security by encrypting data sent over radio waves from one wireless device to another wireless device and by controlling access to network resources through authentication protocols. Only devices that share the same WPA settings as the printer will be able to communicate with the printer. WPA uses encryption keys that change frequently. WPA provides better security than WEP. 4.3 Wired Ethernet networking For setup information, click one of the following options: • Ethernet basics • Installing the printer on an Ethernet network For a description of the printer's Ethernet feature, click one of the following options: • Ethernet lights • Report Page button • Network icon • HP Report page • Embedded Web server (EWS) Other information: • Resetting the printer to the factory defaults • Troubleshooting • Glossary 45