HP Xw6200 HP Workstation xw6200 Service and Technical Reference Guide (3rd Edi - Page 89
PCI Express, interfaces e.g. PCI.
 |
UPC - 882780333536
View all HP Xw6200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 89 highlights
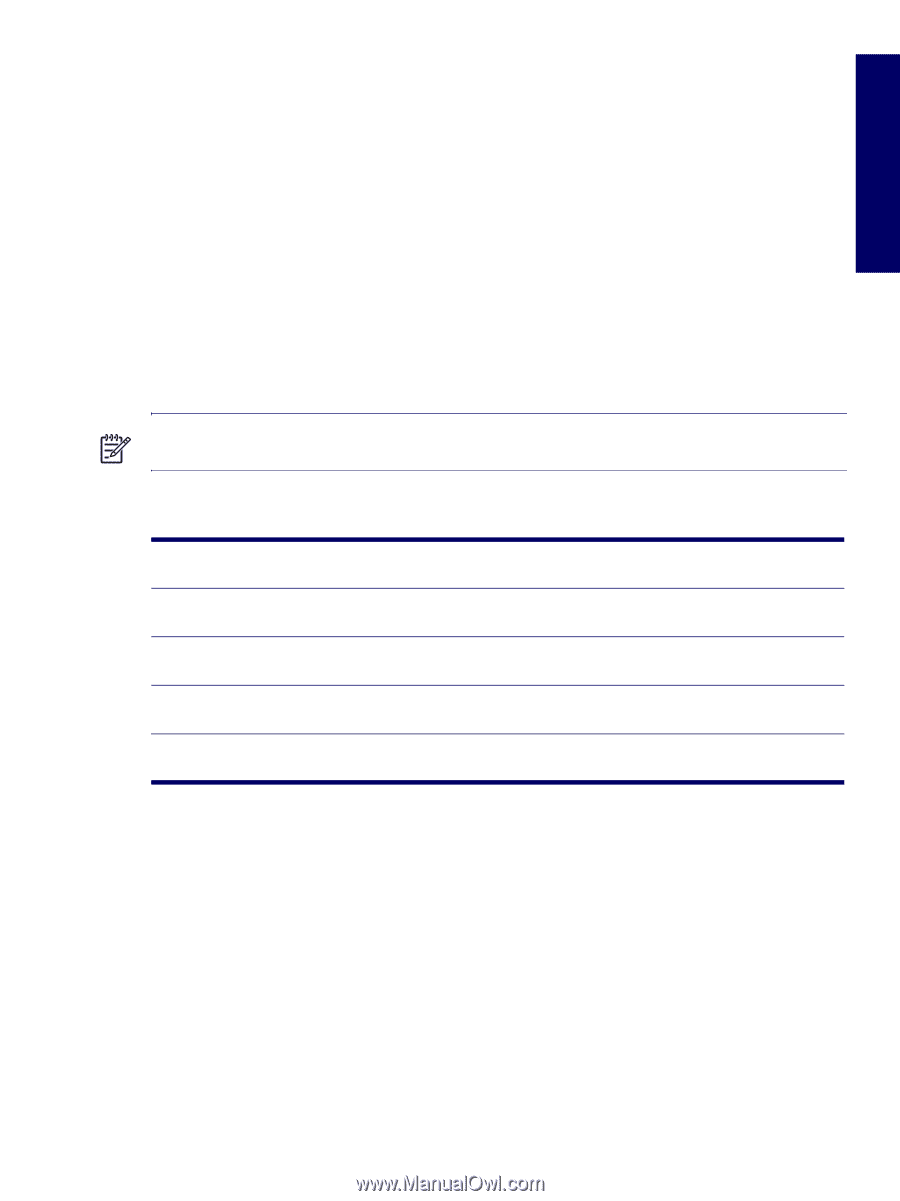
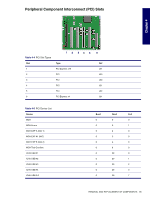
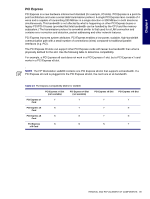
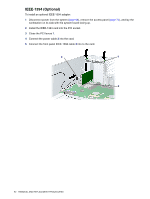
Chapter 4 PCI Express PCI Express is a new hardware interconnect standard (for example, I/O slots). PCI Express is a point-topoint architecture and uses a serial data transmission protocol. A single PCI Express lane consists of 4 wires and is capable of transmitting 250 MB/sec in a single direction or 500 MB/sec in both directions simultaneously. This bandwidth is not affected by what is happening on other PCI Express buses or legacy PCI/PCI-X buses (provided that total bandwidth can be handled by the CPU and the memory subsystem.) The transmission protocol is somewhat similar to that used for a LAN connection and contains error correction and detection, packet addressing and other network features. PCI Express improves system attributes. PCI Express enables a low-power, scalable, high-bandwidth communication path with a small number of connections (wires) compared to traditional parallel interfaces (e.g. PCI). The PCI Express IO slots can support other PCI Express cards with lesser bus bandwidth than what is physically defined for the slot. Use the following table to determine compatibility. For example, a PCI Express x8 card does not work in a PCI Express x1 slot, but a PCI Express x1 card works in a PCI Express x8 slot. NOTE The HP Workstation xw6200 contains one PCI Express x8 slot that supports x4 bandwidth. If a PCI Express x8 card is plugged into the PCI Express x8 slot, the card runs at x4 bandwidth. Table 4-6 PCI Express Compatibility Matrix for xw6200 PCI Express x1 Slot (not available) PCI Express x4 Slot (not available) PCI Express x1 Y Y Card PCI Express x4 N Y Card PCI Express x8 N N Card PCI Express N N x16 Card PCI Express x8 Slot PCI Express x16 Slot Y Y Y N Y N N Y REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENTS 89