Linksys WCG200 User Guide - Page 43
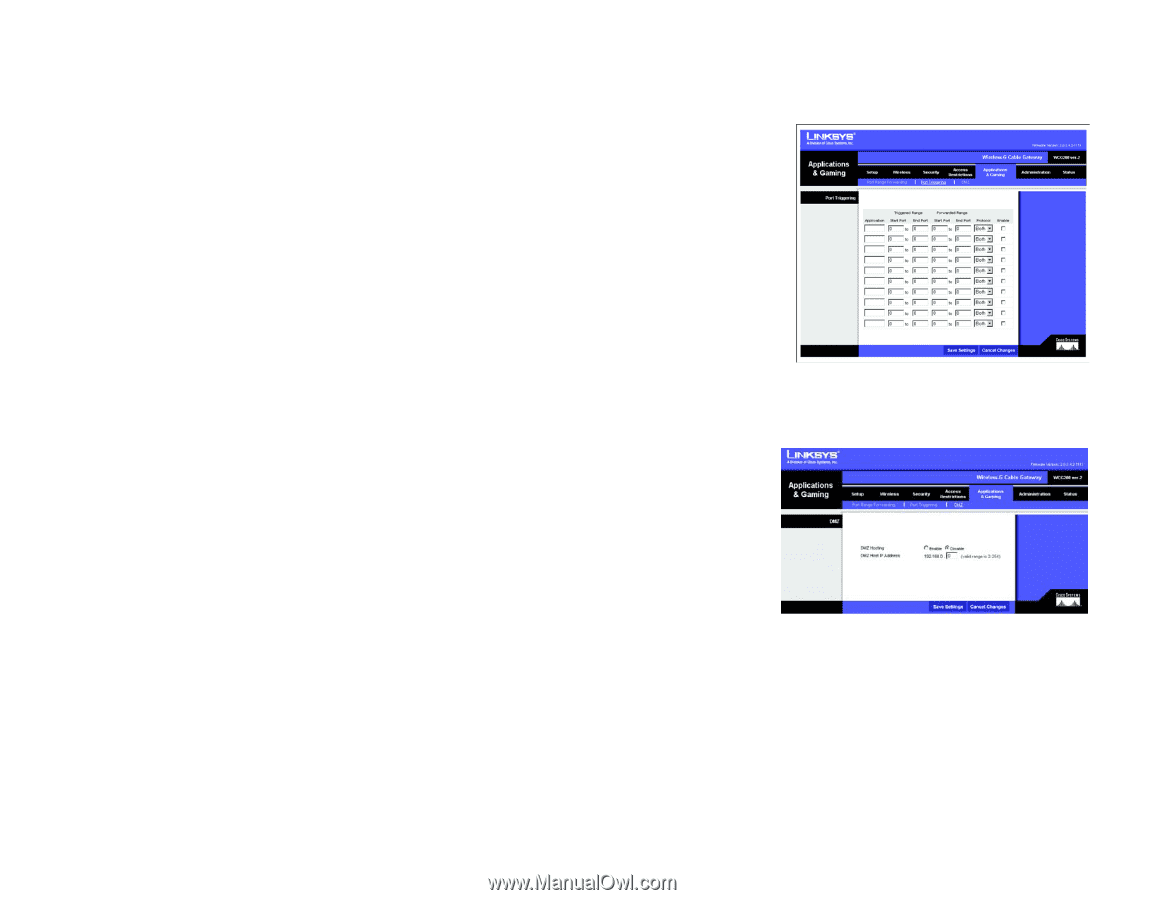
Port Triggering
 |
UPC - 745883583935
View all Linksys WCG200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
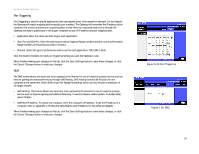
Wireless-G Cable Gateway Port Triggering Port Triggering is used for special applications that can request a port to be opened on demand. For this feature, the Gateway will watch outgoing data for specific port numbers. The Gateway will remember the IP address of the computer that sends a transmission requesting data, so that when the requested data returns through the Gateway, the data is pulled back to the proper computer by way of IP address and port mapping rules. • Application. Enter the name you wish to give each application. • Start Port and End Port. Enter the starting and ending Triggered Range numbers and the Incoming Forwarded Range numbers of the port(s) you wish to forward. • Protocol. Select the type of protocol you wish to use for each application: TCP, UDP, or Both. Click the Enable checkbox for each port triggering setting you want the Gateway to use. When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes. DMZ The DMZ screen allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for use of a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming and videoconferencing through DMZ Hosting. DMZ hosting forwards all the ports for one computer at the same time, which differs from Port Range Forwarding, which can only forward a maximum of 10 ranges of ports. • DMZ Hosting. This feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for use of a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming and videoconferencing. To use this feature, select Enable. To disable DMZ, select Disable. • DMZ Host IP Address. To expose one computer, enter the computer's IP address. To get the IP address of a computer, refer to "Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter." When finished making your changes on this tab, click the Save Settings button to save these changes, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes. Chapter 5: Configuring the Wireless-G Cable Gateway The Applications and Gaming Tab Figure 5-25: Port Triggering Figure 5-26: DMZ 37